Table of contents
Table of contents
Your complete guide to product specifications

Page Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
- What product specifications are and why they’re critical to successful product development
- The different types of product specifications, from requirements and features to technical, design, and compliance standards
- Who creates and uses product specifications, and how they ensure alignment across teams
- The key principles of writing clear, precise, and consistent specifications
- How to create a complete product specification document step by step, with practical examples
- Best practices to avoid common pitfalls and keep your specs actionable and up to date
- Real-world examples of product specifications across industries like electronics, software, and apparel
- How platforms like Miro simplify the product specification process through collaboration, visualization, and iteration
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Creating a successful product begins with a clear plan. Product specifications serve as the foundation for aligning teams, guiding development, and ensuring the final product meets expectations. Whether you’re working in software, manufacturing, or design, understanding how to craft an effective product specification is essential.
This guide will help you master what product specifications are, why they matter, and how to create a document that ensures success.
What are product specifications?
A product specification is a document that outlines a product’s requirements, features, and standards. It defines:
- What the product is
- How it should function
- The criteria it must meet
Specs aren’t limited to one type of product, they apply equally to physical goods, digital platforms, and even services.
- For a physical product like a smartphone, specs might detail screen size, materials, and battery life.
- For a digital product like a SaaS tool, they could cover user flows, performance benchmarks, and security requirements.
- For a service, specifications might outline processes, delivery standards, or compliance needs.
By capturing these details upfront, specs act as a blueprint for product development. They help teams involved in the process align on the same vision and work toward the same goal. These documents are critical across industries, from consumer electronics to SaaS platforms.
Importance of product specifications
Having clear and thorough product specifications isn’t just helpful—it’s essential. Here’s why they play a crucial role in product development:
Alignment across teams
Product specifications act as a single source of truth for stakeholders, designers, and engineers. Everyone works from the same document, reducing misunderstandings and ensuring alignment on objectives.
When all teams are aligned, projects stay on track, leading to fewer delays and miscommunications. This alignment is especially critical when working across departments or with external vendors.
Improved efficiency
When every requirement is clearly outlined, teams can execute tasks more efficiently. Detailed specifications prevent miscommunications and minimize costly revisions or delays. Teams can use the document as a reference point to resolve uncertainties quickly, saving time and resources.
Better quality control
A product specification provides measurable criteria for assessing quality. By defining standards upfront, teams can identify and address issues before the product reaches the market. This proactive approach ensures that products meet customer expectations and minimize returns or complaints.
Compliance and safety
Meeting legal, safety, and regulatory requirements is non-negotiable. Specifications ensure products comply with applicable standards, avoiding expensive delays or rework. Clear compliance guidelines protect companies from potential legal challenges and ensure consumer trust.
Who writes and uses product specs?
Product specifications are rarely created in isolation. While product managers often take the lead in drafting specs, they’re shaped and refined by input from many stakeholders.
- Product managers usually own the document, defining goals, features, and priorities.
- Designers use specs to understand user needs, map experiences, and ensure the product is intuitive.
- Engineers and developers rely on specs for technical requirements, system constraints, and implementation details.
- QA teams test against the specifications to confirm that the final product matches what was agreed.
- Marketing and sales teams use specs to position the product accurately and set expectations for customers.
In practice, specs are a communication tool, not just for the person who writes them, but for every team that touches the product.
Key principles of product specifications
Crafting effective product specifications requires adherence to key principles. These qualities ensure the document is actionable and practical:
Clear
Clarity prevents misinterpretation. Use unambiguous language, like "heat-resistant up to 500°F," to ensure everyone understands the requirements. A clear specification reduces the risk of errors during production or development, making it easier for teams to execute tasks accurately.
Precise
Precision eliminates guesswork. Instead of stating "small size," specify exact dimensions like "2.5 inches in diameter." Precise details help manufacturers and developers avoid missteps that could lead to costly rework.
Consistent
Consistency in terminology, units, and formatting throughout the document avoids confusion and keeps all teams on the same page. For example, using the same unit of measurement throughout ensures clarity for global teams or vendors.
Types of product specifications
Different products demand unique specifications. Here are some key types of product specifications and their purposes:
Requirement specifications
Define why the product exists. Requirements specifications define the purpose, goals, and user needs that shape development. For example, the purpose might state, “This product will streamline data analysis for mid-size companies.”
By clearly documenting requirements, teams stay aligned on priorities, reduce scope creep, and ensure features tie back to real user and business needs. A Product Requirements Document (PRD) is a common way to structure this information.
Features and functional specifications
List what the product needs to do. Features might include specific functionalities, such as "voice activation for hands-free operation." Including prioritized features ensures that teams focus on delivering the most critical capabilities first.
Design specifications
Outline physical and aesthetic requirements as part of your product design specification, such as materials, dimensions, or colors. For example, "polycarbonate casing with matte finish" provides clear guidance.
These details ensure the final product meets both functional and visual expectations.
Performance specifications
Specify benchmarks for performance standards, such as "battery life lasting 10 hours of continuous use." Performance metrics help developers test the product’s capabilities under real-world conditions.
Safety and compliance specifications
Detail legal and safety standards the product must meet. For instance, "FDA approval required for medical use." Including compliance requirements avoids costly redesigns and ensures a smooth market launch.
Technical specifications
Document the technical details that define how the product will work. This may include system architecture, integrations, performance standards, or security requirements. For example, “must support 1,000 concurrent users with 99.9% uptime”.
Clear technical specifications ensure engineering teams have the information needed to build a product that is reliable, scalable, and compliant with standards.
What should a product specification sheet include?
A strong product spec balances clarity, detail, and usability. Here are the key elements you should include:
- Product summary: Describe what the product is, what it does, and why it’s needed. This section sets the vision and acts as a reference point throughout development.
- Features and requirements: Outline what the product must do, how it should work, and any essential materials or technologies needed. Prioritize the most critical features first.
- Timeline and milestones: Capture development phases, key milestones, and delivery dates to keep teams accountable and projects on track.
- Budget considerations: Detail available resources, development costs, and expected spend to align financial and product goals.
- Risks and challenges: Identify potential roadblocks, technical, operational, or market-related, so teams can plan mitigation strategies early.
- Business case: Highlight the product’s expected benefits, ROI, or market impact to secure stakeholder buy-in.
- User stories: Describe functionality from the end-user perspective (e.g., “As a shopper, I want to filter products by price so I can compare quickly.”).
- User personas: Include representative persona profiles of your target audience to ground the spec in real needs and behaviors.
- Functional specs: Provide technical details about how the product works and what support or infrastructure is required.
- Non-functional specs: Document broader expectations like scalability, usability, or security standards.
- Design specifications: Add wireframes, mockups, or design references to give teams and stakeholders a visual understanding of the product.
Building your spec in Miro makes it easy to capture all these elements in one place. You can layer user personas next to features, attach wireframes, and invite stakeholders to comment directly on the spec.
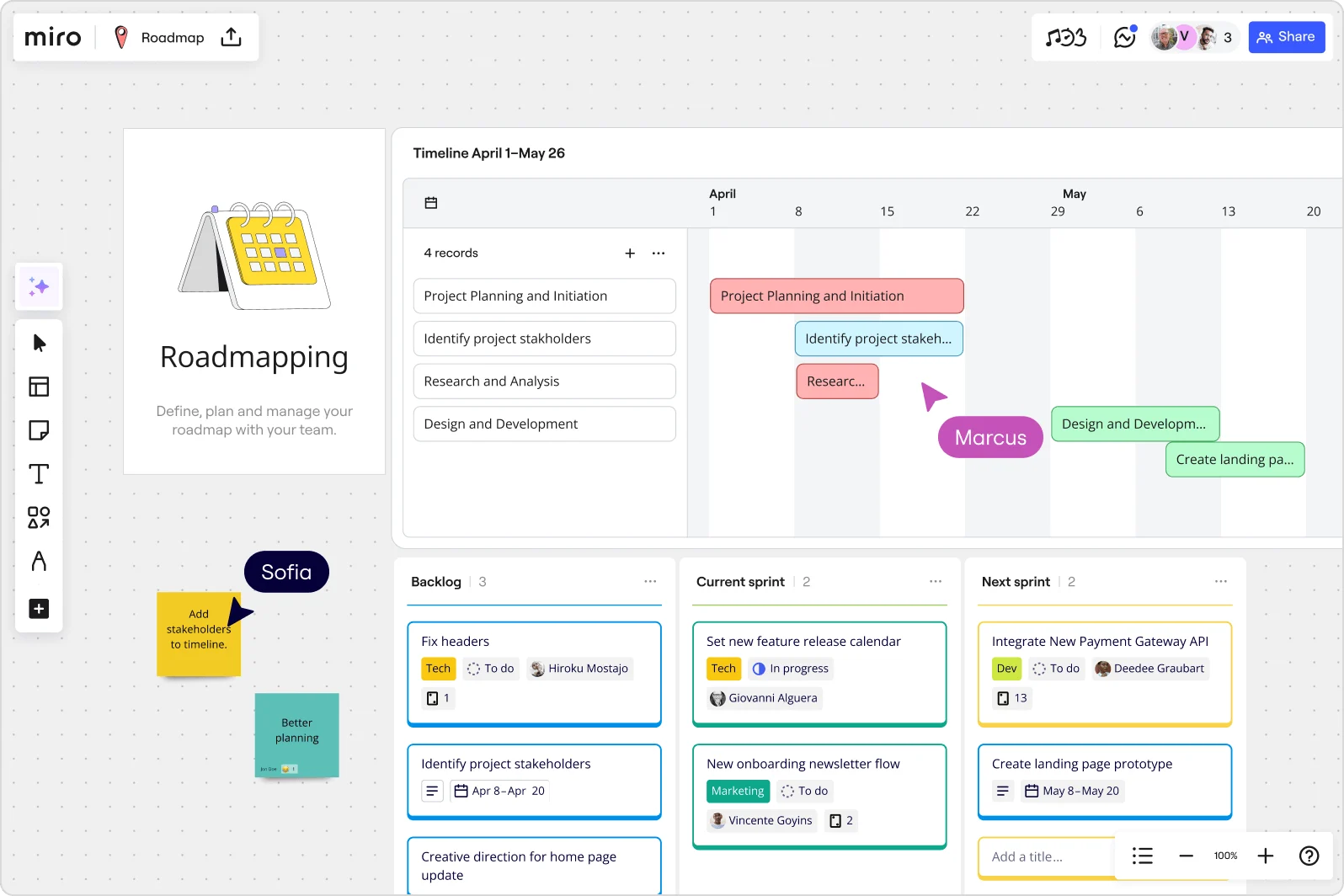
How to create a product specification document
A well-constructed product specification document takes planning and collaboration. Follow these steps to ensure your document sets the stage for success:
1. Define the purpose
Start with a clear purpose statement that answers: Why are we creating this product? What problem or challenge will it solve for users? What business need does it support? A strong purpose ties the product directly to user pain points and measurable outcomes.
Capture these needs in the product summary so every feature, decision, and trade-off connects back to solving the right problem. In Miro, you can capture insights from workshops, cluster feedback with AI, and map problems visually, giving your team a clear foundation that guides every decision during the development process.
2. Outline features and functionality
List every feature the product requires, but don’t stop there—connect them to what customers actually need. Be specific and prioritize essential functions that solve real problems. Use customer feedback from existing or related products to guide decisions. This ensures your spec reflects not only what the product will do, but how it will help your target users.
In Miro, you can import that feedback directly onto the board, turn it into user stories, and run quick prioritization exercises like dot-voting to align on what matters most.
3. Detail technical and design requirements
Include precise measurements, materials, and technical details that guide the production or development process. For example, specify whether the product should use stainless steel or lightweight aluminum.
With Miro, you can pull in wireframes, diagrams, or design assets, and group them alongside system requirements so technical and design teams work from the same visual source of truth.
4. Address compliance needs
Research applicable regulations or certifications and document them to ensure market readiness. Ignoring compliance can lead to delays or rejections during the approval process.
Storing compliance checklists, certifications, and risk assessments in Miro keeps everything centralized, while comments and tags make it easy to assign ownership across teams.
5. Collaborate with stakeholders
Involve all relevant teams early in the process to gather diverse input and identify potential challenges. Collaboration ensures that the document reflects the needs and expertise of every department.
Miro supports both real-time and async feedback, so engineers, designers, and stakeholders can contribute on their own schedules. Features like @mentions, voting, and integrations with Slack or Confluence help keep conversations and decisions visible to everyone.
6. Prototype and run user tests
Once the core features are defined, build a prototype to validate your assumptions. Put it in front of real users and watch how they interact with it. Are the most important tasks easy to complete? Do they find certain features confusing, unnecessary, or missing altogether?
Capture what feels intuitive and what causes friction. These insights help you refine requirements before development begins, saving time and reducing costly rework. With Miro, you can map user flows, gather feedback directly on prototypes, and keep findings linked to your product spec for easy iteration.
7. Review and refine
Treat your specification document as a living document. Regularly review and update it as the project evolves to maintain its relevance and accuracy. Because Miro integrates with Jira and Confluence, updates flow directly into your delivery tools, while version history and centralized comments ensure the latest spec is always the single source of truth.
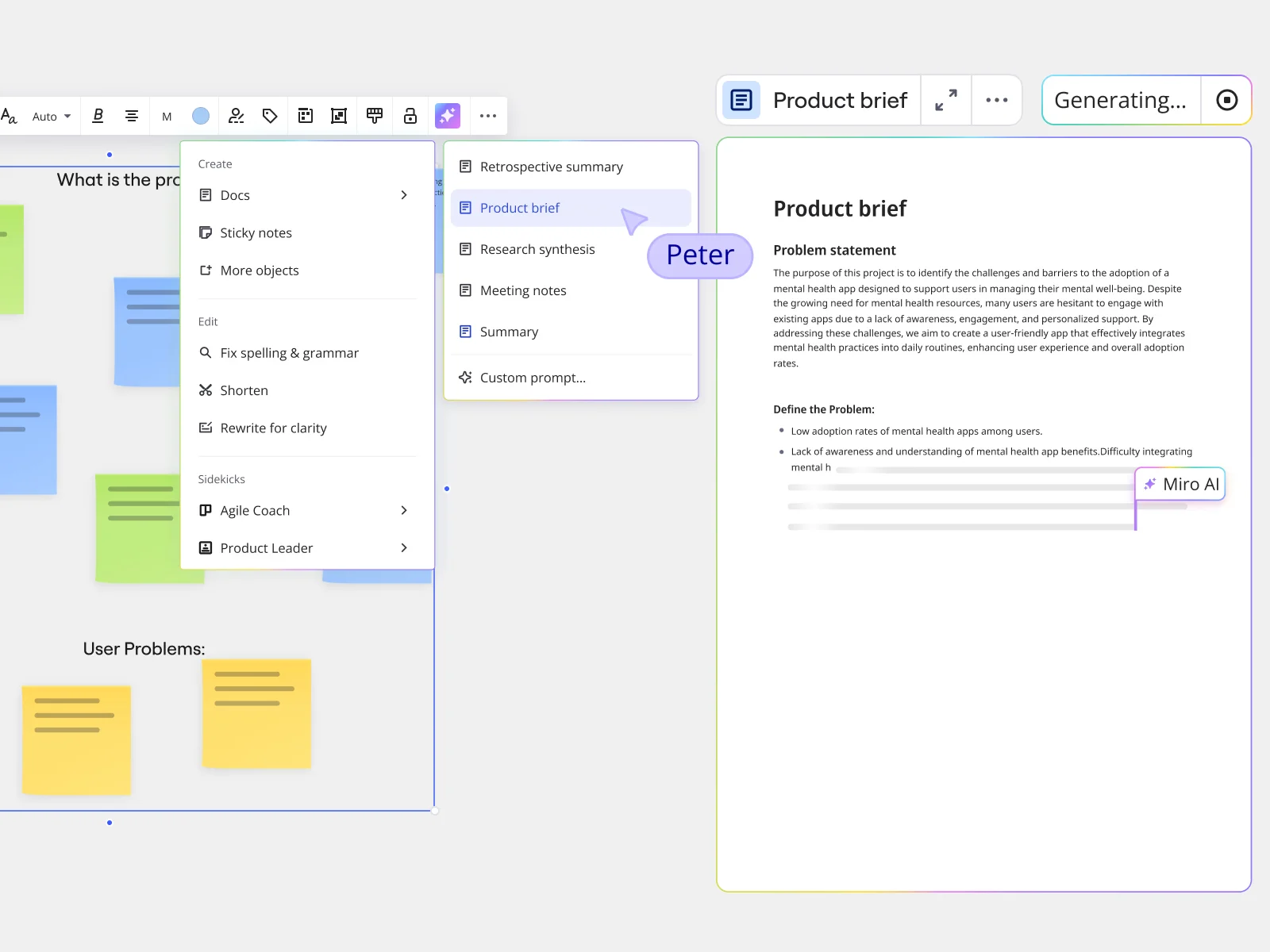
Best practices in product specifications
Even seasoned teams can make mistakes when creating product specifications. Avoid these common pitfalls by applying the following best practices:
Use clear descriptions
Vague descriptions lead to confusion and errors. Always provide explicit instructions and details. For example, instead of saying “lightweight,” specify the exact weight range the product should fall within.
Add stakeholder input
Failing to involve key stakeholders can result in overlooked requirements and misaligned priorities. Regular input from teams ensures the document meets everyone’s needs.
Avoid overloading details
Adding irrelevant details can clutter the document and confuse teams. Focus on essentials. For instance, avoid including lengthy background information that doesn't contribute to actionable guidelines.
Keep it up-to-date
Product specifications must evolve alongside the project. Ignoring updates can lead to discrepancies that derail progress. Regular revisions help teams stay aligned with any new developments.
Real-world product specification examples
Effective product specifications vary by industry but share the same core purpose: to provide clarity and guidance. Here are some real-world examples:
Electronics
A smartphone specification might include "OLED screen, 6.5 inches, with Gorilla Glass protection" to ensure consistency in production.
Apparel
A clothing spec might define the fabric as "100% organic cotton, with double-stitched seams for durability." This ensures quality and consistency in manufacturing
Software
A SaaS platform specification could include user requirements like "dashboard loads in under 2 seconds" to meet user expectations and performance benchmarks.
WebMD - delivering healthcare solutions faster
WebMD’s product teams needed a way to move beyond traditional waterfall processes and accelerate the delivery of digital healthcare solutions. The challenge was aligning cross-functional stakeholders while capturing detailed requirements and user insights without slowing down development.
By adopting Miro, WebMD built a more collaborative product specification process. Teams could map out user journeys, document requirements, and validate assumptions in one shared space—ensuring nothing was lost between discovery and delivery.
As one team member explained: “Before Miro, each different team had its own workflow. Now that we’re all using the same template in Miro, I’m able to jump into any project and know exactly where the team is at in the process.”
This shift empowered WebMD to test ideas earlier, align stakeholders quickly, and iterate on specifications with greater clarity.
The results?
- Faster product delivery cycles with improved alignment
- 60% more product improvements each quarter
- Stronger engagement and adoption across healthcare users and providers
Simplify product specification documentation in Miro
Simplify your product specification process with Miro’s innovation workspace. Use our AI-powered visual canvas to brainstorm, collaborate, and refine your product specifications with ease. From aligning teams to sharing updates in real-time, Miro helps you stay organized and productive.
Key takeaways
- A product specification is the blueprint that connects user needs, business goals, and delivery teams.
- Strong specs are clear, measurable, and user-focused, helping avoid rework and misalignment.
- Collaboration is critical - product managers, engineers, designers, QA, and stakeholders all contribute to a complete spec.
- Treat your spec as a living document: review, refine, and update as the project evolves.
Ready to write your next product specification? Try Miro today and bring clarity, collaboration, and speed to your process.
Product specification FAQs
What is the difference between a product specification document and a product requirements document (PRD)?
A product specification document describes what the product is—outlining its features, functions, materials, design details, and performance standards. It acts as a blueprint, giving teams clarity on how the product should look, feel, and behave.
A product requirements document (PRD), on the other hand, explains why the product is being built and what problems it should solve. It captures objectives, user needs, and high-level requirements, serving as a strategic guide for development.
Both documents complement each other: the PRD sets direction, and the product spec ensures the vision is executed correctly.
How are product specifications validated?
Validation happens through testing and feedback. Once a draft specification is written, teams review it with stakeholders and, where possible, test prototypes against the requirements. This helps confirm that the document reflects real user needs and is technically feasible. Tools that allow for linked prototypes and async feedback, like Miro, can accelerate this process.
How do you manage changes in a product specification?
Change is inevitable as products evolve. The best approach is to treat specs as living documents: record updates in a shared workspace, note why changes were made, and notify all stakeholders. This keeps everyone working from the same source of truth and reduces the risk of misalignment.
Can I use product specification software to help me?
Yes, product specification software can make the process much easier. Instead of working with static documents or scattered files, these tools give teams a single, collaborative space to create, edit, and share specs. Good software helps you:
- Standardize specs with templates so nothing gets missed
- Invite stakeholders to contribute in real time or asynchronously
- Link supporting research, prototypes, and user stories in one place
- Track updates so the document always reflects the latest decisions
What is the difference between a product design specification and product specifications?
A product specification describes the overall vision for a product—its goals, features, and performance requirements. It ensures all teams share a common understanding of what needs to be built.
A product design specification (PDS) is a type of product specification that zooms in on design details. For physical products, this might include dimensions, materials, or durability; for digital products, it could cover UI components, accessibility, or interaction patterns.
In other words, every PDS is a product specification, but not every product specification is a PDS. The PDS narrows in on design, while broader product specs can cover functionality, business needs, or technical requirements.
Are there ready-made templates for product specifications?
Yes. Miro provides Product Specification and PRD templates, plus thousands of community-created boards in Miroverse. You can adapt proven workflows from other teams, saving time and ensuring your specs follow best practices.
Is Miro easy for new teams to use when creating product specifications?
Absolutely. Miro’s templates guide you step by step, so even teams new to specification writing can get started quickly. The intuitive canvas makes it simple to capture requirements, link user stories, and organize details without a steep learning curve.
Can Miro handle large or complex product specifications?
Yes. With Miro’s infinite canvas, you can start small with a single product spec and expand into detailed branching documents. Duplicate frames for multiple products or versions, and connect requirements across discovery, design, and delivery without losing context.
Is Miro easy for new teams to use when creating product specifications?
Absolutely. Miro’s templates guide you step by step, so even teams new to specification writing can get started quickly. The intuitive canvas makes it simple to capture requirements, link user stories, and organize details without a steep learning curve.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 23, 2025