Three-Hour Brand Sprint Template
Turn abstract ideas about your brand into common language. Evaluate your brand positioning during a 3-hour brand sprint.
Trusted by 65M+ users and leading companies
About the Brand Sprint template
A brand sprint is a three-hour meeting comprising six activities to align your team with your motivation, values, audience, personality, and competitive landscape.
After completing the brand sprint workshop and filling in the template, your team will have a simple cheat sheet that will help you communicate your branding philosophy and work more seamlessly in-house or with a branding agency.
Keep reading to learn more about branding and how to run a three-hour brand sprint.
What is a brand sprint?
A brand sprint is an exercise that allows you to distill your disparate ideas about your brand into a comprehensive profile. By answering a series of questions about your brand, you clarify your brand's mission statement, roadmap, and much more.
Brand-building is a high-stakes task. Organizations live or die on how customers and potential customers respond or connect to their brand. Whether your company is building a brand from the ground up or revamping an existing brand, a brand sprint is a valuable tool.
Why use a brand sprint template?
People use a brand sprint template to build a profile for the organization. Brand sprints enable you to think about your roadmap for the future, your values, your audiences, and why your company exists in the first place.
These exercises help you define the attitude and style of your brand and compare your brand to companies operating in the same space.
How to run a Three-Hour Brand Sprint
Running a three-hour brand sprint is not easy, but anyone can be a brand sprint facilitator and help with the prep work.
You should generally aim for two to six people for the three-hour brand sprint, including your CEO. Ideally, the co-founder, marketing, or product head should also be in this meeting.
Designate someone as the “decider” and find one or two extra facilitators to help whoever leads the brand sprint.
If you are the brand sprint workshop facilitator, schedule a block of time where you and your team can work uninterrupted. As the name implies, most brand sprints take about 3 hours.
To start, select Miro’s Brand Sprint template. This will be your framework. Then, follow the steps:
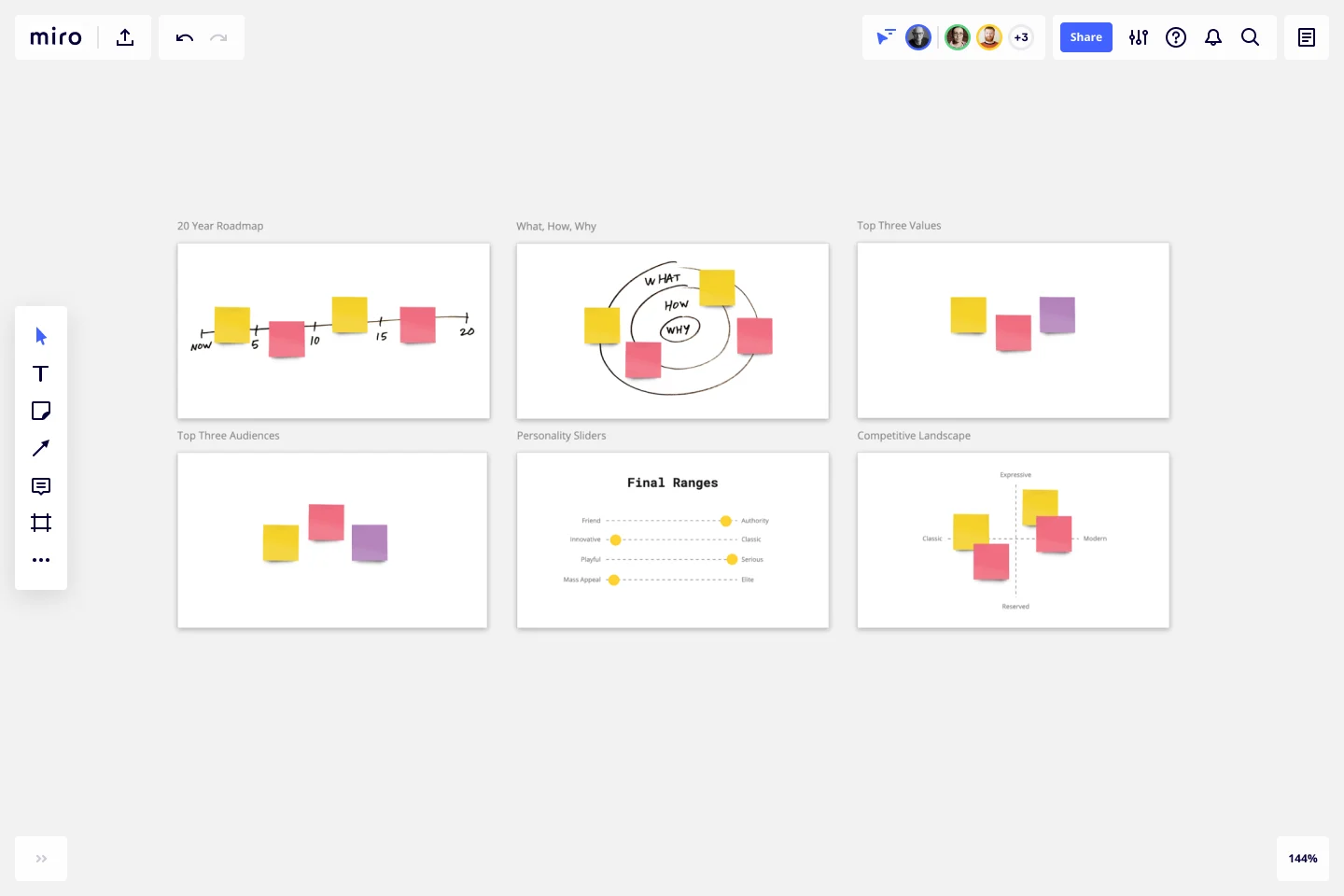
Step 1: 20 Year Roadmap Have each participant write down their own version of that roadmap, then invite everyone to share it. Of course, these don’t have to be exact; no one has a time machine! But this exercise should get you to think about the lifetime of your brand.
Step 2: What, How, and Why
The “What, How, Why” framework consists of three concentric circles. The outside circle is labeled “what,” the middle circle is “how,” and the inside circle is “why.”
Go around the room and ask everyone to answer three fundamental questions:
What does your company do?
How do you do it?
And why?
Step 3: Top Three Values
Write down your company’s top three values. Rank the decision-making principles that matter to you.
You can set a timer for this section and ask participants to vote on the values they most agree with.
Step 4: Top Three Audiences
List your top three audiences. Have everyone in the room write down their own answers to this question, then bring everyone together to share.
Step 5: Personality Sliders
Now it’s time to start thinking about your brand’s attributes. The Personality Sliders exercise invites you to position your company’s attributes between brand extremes, such as Friendly and Authority or Mass Appeal and Elite.
Step 6: Competitive Landscape
Finally, analyze your competitive landscape. Ask your team these questions:
What other organizations are operating in your space?
What are they doing right?
What can you do differently?
Where did the brand sprint originate?
The brand sprint was popularized by the team at Google Ventures and written about in detail by Jake Knapp in the book Sprint. The ideas included in the brand sprint come from various sources, including Steve Jobs’s 1997 internal meeting at Apple, Stewart Butterfield’s essay We Don’t Sell Saddles Here, Simon Sinek’s TED talk How Great Leaders Inspire Action.
Want to learn more about the nuts and bolts of running a brand sprint? Read about how Miro went through the brand sprint process during a rebrand with a remote team.
How do you define brand strategy?
A brand strategy is a long-term plan for developing a brand, and the ultimate goal is to have your consumers identify with it and choose your brand instead of others. Businesses and organizations run brand sprints to set the stage for their brand strategy.
How do I know my brand personality?
Running a brand sprint is a great way to discover your brand personality. You can find out about your brand attributes after doing a Personality Slider exercise that invites you to position your organization between brand extremes such as Friend and Authority, or Mass Appeal and Elite. Using adjectives and mood boards will help you and your team identify your brand personality during your branding sprint.
When should you run a brand sprint?
The Google Ventures team recommends only running a brand sprint when you have a trigger event such as naming your company, designing a logo, hiring an agency, or writing a manifesto.
Executive Summary Template
Works best for:
Leadership, Project Management, Documentation
Pique their curiosity. Get them excited. Inspire them to keep reading, diving further into your proposal details. That’s what a good executive summary has the power to do—and why it’s a crucial opening statement for business plans, project plans, investment proposals, and more. Use this template to create an executive summary that starts building belief, by answering high-level questions that include: What is your project? What are the goals? How will you bring your skills and resources to the project? And who can expect to benefit?
Go-to-Market Strategy Template
Works best for:
Marketing, Desk Research, Strategic Planning
It doesn’t matter how innovative or effective a new product is — if it doesn’t get noticed and adopted by the right audience, the product won’t get off the ground. That’s where your Go-to-Market Strategy comes in. It’s a single resource that houses all of your research, insights, and data, and includes your business plan, target audience, marketing approach, and sales strategy. A GTM is especially important for any startups who grow fast, have to make split-second decisions, and have to be fully in sync.
Assumption Grid Template
Works best for:
Leadership, Decision Making, Strategic Planning
Someone wise once said that nothing in life is certain. But the waters of the business world? It can seem especially uncertain and unclear. An Assumption Grid can help you navigate those waters and make your decisions confidently. It organizes your business ideas according to the certainty and risk of each — then your team can discuss them and make judgment calls, prioritize, mitigate risk, and overcome uncertainties. That’s why an Assumption Grid is a powerful tool for getting past the decision paralysis that every team occasionally faces.
Kaizen Report Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Operations, Documentation
What makes a great company great? They know that greatness needs to be fostered and maintained — meaning they never stop working to improve. If you’re one of those companies (or aspire to be), a kaizen report is an ideal tool. It creates a simple visual guide to continuous improvement activities on a team, departmental, and organizational level. Using a kaizen report approach, every employee in an organization audits their own processes and understands what they might have overlooked, making this a powerful tool for increasing accountability at all levels.
User Persona Template
Works best for:
Marketing, Desk Research, User Experience
A user persona is a tool for representing and summarizing a target audience for your product or service that you have researched or observed. Whether you’re in content marketing, product marketing, design, or sales, you operate with a target in mind. Maybe it’s your customer or prospect. Maybe it’s someone who will benefit from your product or service. Usually, it’s a whole collection of personalities and needs that intersect in interesting ways. By distilling your knowledge about a user, you create a model for the person you hope to target: this is a persona.
Blue Ocean 4 Actions Framework Template
Works best for:
Leadership, Decision Making, Strategic Planning
For entrepreneurs, so much comes down to new users—how to attract them, impress them, and convert them to loyal customers. This template, designed by the authors of Blue Ocean Strategy: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition Irrelevant, will help you maximize value for you and your customers alike. Using the template’s four steps (divided into easy columns), you’ll easily evaluate your products in more innovative ways and make sure money is being spent in areas that really matter.