Process map templates
Improve clarity and visualize workflows with Miro's Process Map templates collection. These customizable templates enable you to map out each step of a process, identify bottlenecks, and clarify roles and responsibilities.
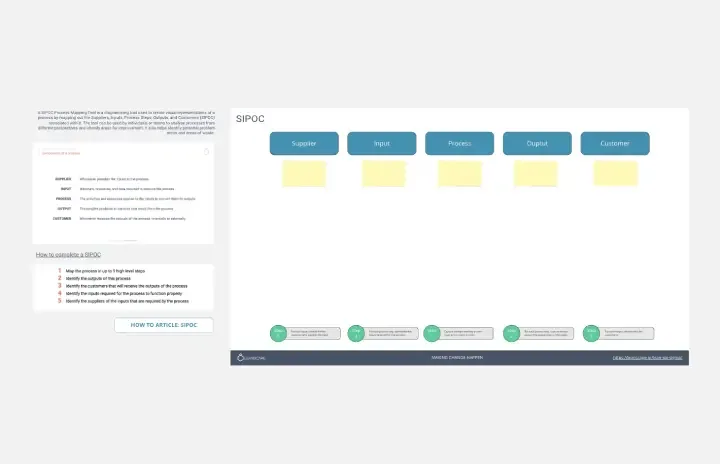
SIPOC Process Map
Works best for:
Agile Metodology
The SIPOC Process Map is a visual tool for documenting the high-level process flow of a system or project. It helps teams identify Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers, facilitating a holistic understanding of the value stream. This template enables teams to visualize key process elements and interdependencies, empowering them to identify areas for improvement and optimize workflow efficiency. By promoting transparency and collaboration, the SIPOC Process Map empowers organizations to deliver value more effectively and satisfy customer needs.
Job Search Process Diagram
Works best for:
Diagramming
The Job Search Process Diagram template offers a visual tool for mapping out the steps and stages involved in the job search process. It provides a structured framework for organizing tasks, tracking progress, and managing resources. This template enables job seekers to streamline their job search efforts, stay organized, and increase their chances of success. By promoting clarity and efficiency, the Job Search Process Diagram empowers individuals to navigate the job market effectively and achieve their career goals.
20/80 Process Diagram - EOS® Compatible
Works best for:
Diagramming
The 20/80 Process Diagram - EOS® Compatible template is a visual tool for mapping out processes and workflows aligned with the Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS®) methodology. It provides a structured framework for identifying core processes and key activities that drive business outcomes. This template enables organizations to streamline operations, clarify roles and responsibilities, and enhance accountability. By promoting alignment with EOS® principles, the 20/80 Process Diagram empowers teams to achieve organizational excellence and drive sustainable growth.
Organization & Process Mapping
Works best for:
Org Charts, Operations, Mapping
The Organization & Process Mapping template facilitates the analysis and optimization of organizational processes. By visualizing process flows, bottlenecks, and handoffs, this template helps teams identify inefficiencies and streamline workflows. With sections for documenting process steps and improvement opportunities, this template empowers teams to implement process enhancements and drive operational excellence.
Fishbone Diagram for Process Improvement
Works best for:
Planning, Strategy
Process improvement is key to enhancing efficiency and productivity. The Fishbone Diagram for Process Improvement template helps you identify the root causes of process inefficiencies. Categorize potential causes into areas such as workflow, resources, technology, and personnel. This structured analysis enables your team to systematically explore and address issues, streamlining processes and boosting overall productivity.
Headcount Approval Process Flowchart
Works best for:
Flowcharts, Mapping, Diagrams
The Headcount Approval Process Flowchart template offers a visual framework for illustrating the steps and stages involved in the headcount approval process within an organization. It provides a structured framework for documenting approval workflows, roles, and decision points. This template enables HR professionals and managers to streamline the headcount approval process, ensure compliance, and improve transparency and accountability. By promoting clarity and efficiency, the Headcount Approval Process Flowchart empowers organizations to manage their workforce effectively and make informed staffing decisions.
BPMN Marketing Process-Launching Smartphone
Works best for:
BPMN
The BPMN Diagram for Marketing Processes template streamlines the launch of new products by visually organizing every step, from market research to campaign execution. Ideal for marketing teams, this template ensures effective communication, optimized workflows, and successful campaign outcomes by providing a clear roadmap for each stage of the marketing journey.
Change Control Process Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Documentation, Product Management
You can predict, research, and plan for every detail of a project to go a certain way—then along comes the unforeseen and modifications are needed. That’s when a change control process comes into play. It helps define the right steps to take, gives stakeholders full visibility, and reduces the chances of errors and disruption. And this template is easy to use and highly effective—for ensuring that proposed changes are reviewed before they’re implemented, and empowering teams to veto changes that might prove unnecessary or disruptive.
Process Map Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Product Management, Mapping
Process mapping allows you to assess, document, and strategize around any plan or approach your team has put in place. It’s a useful tool for eliminating or preventing blockers. Organized by stages, a process map enables your team to divide up a process or system and record deliverables and action items at each stage of the process. By breaking down the objectives, activities and deliverables at any stage of a project, you can gain insight into whether you are on track or effectively working through a problem.
Value Stream Mapping Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Strategic Planning, Mapping
A value stream map can help you refocus your business on steps that actually provide value to your customers, cutting out wasteful and inefficient processes. With this template, you and your process team can collaborate on a value stream map today.
Stage-Gate Process Flowchart Template
Works best for:
Diagramming, Project Management
The Stage-Gate Process Flowchart Template structures a project into distinct stages separated by decision-making gates, enhancing the quality of decisions and leading to more successful project outcomes.
Semantic Map Template
Works best for:
Brainstorming
The Semantic Map Template is a helpful tool that helps teams efficiently process and structure complex information. Its intuitive design promotes shared understanding, allowing multiple users to contribute and refine ideas simultaneously. This collaborative approach streamlines brainstorming sessions and creates a synergistic environment where collective intelligence thrives. By visually mapping out concepts and their interconnections, the template ensures that every team member is on the same page, which improves group dynamics and leads to more cohesive and comprehensive outcomes. The Semantic Map Template is a valuable tool for team-based project management and learning, thanks to its ability to foster collaboration and enhance productivity.
Swimlane Diagram Template
Works best for:
Flowcharts, Diagrams, Workflows
A swimlane diagram shows you which stakeholders are responsible for each area of your critical processes. You can use it to understand current processes or plan new ones.
Design Process Flowchart Template
Works best for:
Flowchart, Diagramming
The Design Process Flowchart Template is an excellent tool to navigate the complexities of a design project. It offers a clear and organized visual representation of each step in the design journey, making it easier to understand and follow. One of its key benefits is that it enhances team collaboration. By providing a visual outline of the design process, the template fosters a shared understanding among team members, regardless of their individual roles or expertise. This common visual framework enables more efficient communication, aligning everyone's efforts toward a unified goal. As a result, it not only streamlines the workflow but also encourages collective creativity and innovation, which are essential elements in any successful design project.
Strategic Group Mapping Template
Works best for:
Mapping, Strategy
The Strategic Group Mapping Template is a cutting-edge visual tool designed to translate the competitive landscape of their industry. By allowing users to plot entities based on distinct criteria, this template provides an at-a-glance view of market dynamics. One standout benefit of using this tool is its ability to identify clusters of competitors and market gaps, paving the way for businesses to strategically position themselves for optimal success.
On-Premise to Cloud Migration Process Flowchart Template
Works best for:
Flowcharts
The On-Premise to Cloud Migration Process Flowchart Template is a strategic tool designed to streamline the transition from traditional on-premise systems to more flexible, scalable cloud-based solutions. This template acts as a visual roadmap, guiding teams through each phase of the migration process with clarity and precision. By breaking down the migration into manageable steps, it ensures a comprehensive approach, minimizing risks and aligning with best practices for cloud adoption.
Join thousands of teams collaborating and doing their best work on Miro.
Sign up freeAbout the Process Map Templates
A process map template is valuable to document, analyze, and better understand your team’s business processes and associated outcomes. This process map template is organized by stages to help you record the objectives, activities, and deliverables during each step of a process. Use the template to improve your team’s organization, productivity, and communication by coming to a shared understanding of any kind of process.
What is the purpose of process mapping?
You would never think about setting out into the unknown without a map. A process map is no different. Process mapping is an effective exercise to assess, document, or strategize around any plan or approach your team might have. By breaking down the objectives, activities, and deliverables at any stage of a project, you can gain insight into whether you are on track or effectively working through a problem.
When to use the process mapping template
These process map examples are set up to help teams increase efficiency. By seeing a process laid out on the page, teams can identify areas for improvement: how to streamline the process, improve communication, and create better documentation. Use process mapping tools when you need to assign stakeholders, define ownership and boundaries, clarify responsibilities, and establish metrics.
How to use the process map templates
The goal of process mapping is to break down your project so that your teammates understand your objectives and how you plan to achieve them. By dividing the project into stages, you can avoid misunderstandings and ensure everyone is aligned before moving forward. Follow these steps to use the process map template:
Step 1: Define your goal
What is the problem you would like to solve? What’s the process you would like to visualize?
This is the time to think big. As you advance through your process map template, you’ll spend more and more time cutting your project up into bite-sized chunks. For now, though, feel free to set a broad goal.
Step 2: Brainstorm
What steps will you need to take to solve this problem? How will the process unfold?
Don’t get too bogged down in the order you must undertake the process. Focus on getting all the steps down on the board. Think about the stakeholders you will need to involve in this project. You can also brainstorm resources you’ll need to get the job done.
Step 3: Define success
How will you know when you’ve solved the problem? When is the process over?
Many teams skip this step, but it’s important not to neglect it. By defining clear metrics for success ― or even just a stopping point ― you give yourself something to work toward.
Step 4: Put things in order
What steps will you take to solve the problem? What is the order in which you must work to make sure the process gets done?
Now is the time to think linearly. Take all the raw material from your brainstorm and start putting things in order. If it’s too daunting to work linearly, start by defining what you’ll need to do first and last, and then work on everything in between.
Step 5: Draw it out
What does the problem look like? How can you visualize the process?
It’s time to put your process map template to work. Start by creating a key. The key should contain symbols that you’ll use throughout the process map.
You might need symbols representing activities, inputs, outputs, decisions, and endpoints. Use a system that is intuitive and scalable. For example, many people like to use arrows to indicate the flow of decision-making.
Step 6: Review the map
Are you in a good position to solve the problem? Does the process map look actionable and digestible?
Invite stakeholders to interrogate the map. Pay close attention to possible redundancies, bottlenecks, and problems with workflow. Go over each step to make sure they flow logically from one another. It might help to return to the documents from your brainstorm and make sure nothing was lost in translation.
Explore all template categories to find the perfect tools for brainstorming, planning, collaboration, and execution—designed to streamline your workflow and bring your ideas to life.