Work Plan Template
Define the milestones of a project and create a detailed plan to achieve your goals.
About the Work Plan Template
Miro’s work plan template is a free and fully customizable visual roadmap you can start using to plan your projects. It outlines the steps you should take to achieve the desired goal, sets demonstrable objectives, and establishes measurable deliverables. An effectively completed work plan template guides you throughout the project lifecycle, allowing you to realize an outcome by collaborating with your team.
While the work plan template is a powerful tool for project management on its own, you can also incorporate the Lean Six Sigma methodology to enhance your experience. Lean Six Sigma is an approach to streamlining business processes that originated in the manufacturing industry. It aims to reduce waste, improve quality, and increase efficiency and product value.
We’ll walk you through more tips to make the most out of Miro’s work plan template.
How to use Miro’s work plan template
To get started, scroll to the top of this page and click on the blue “Use template” button. That’ll allow you to access the work plan template in Miro. Once you’re in, here are a few steps you can take:
1. Align on goals and strategy
Before you can start filling the work plan template in, make sure you’ve got a clear goal you’re working towards. Gather input from team members, stakeholders, and project sponsors — including information about your project timeline, resources, constraints, and key deliverables you’d like to have.
Want to collaborate on the work plan template? Invite team members to edit your Miro board together with you in real-time by clicking on the blue “Share” button on the top right.
2. Add tasks to the work plan template
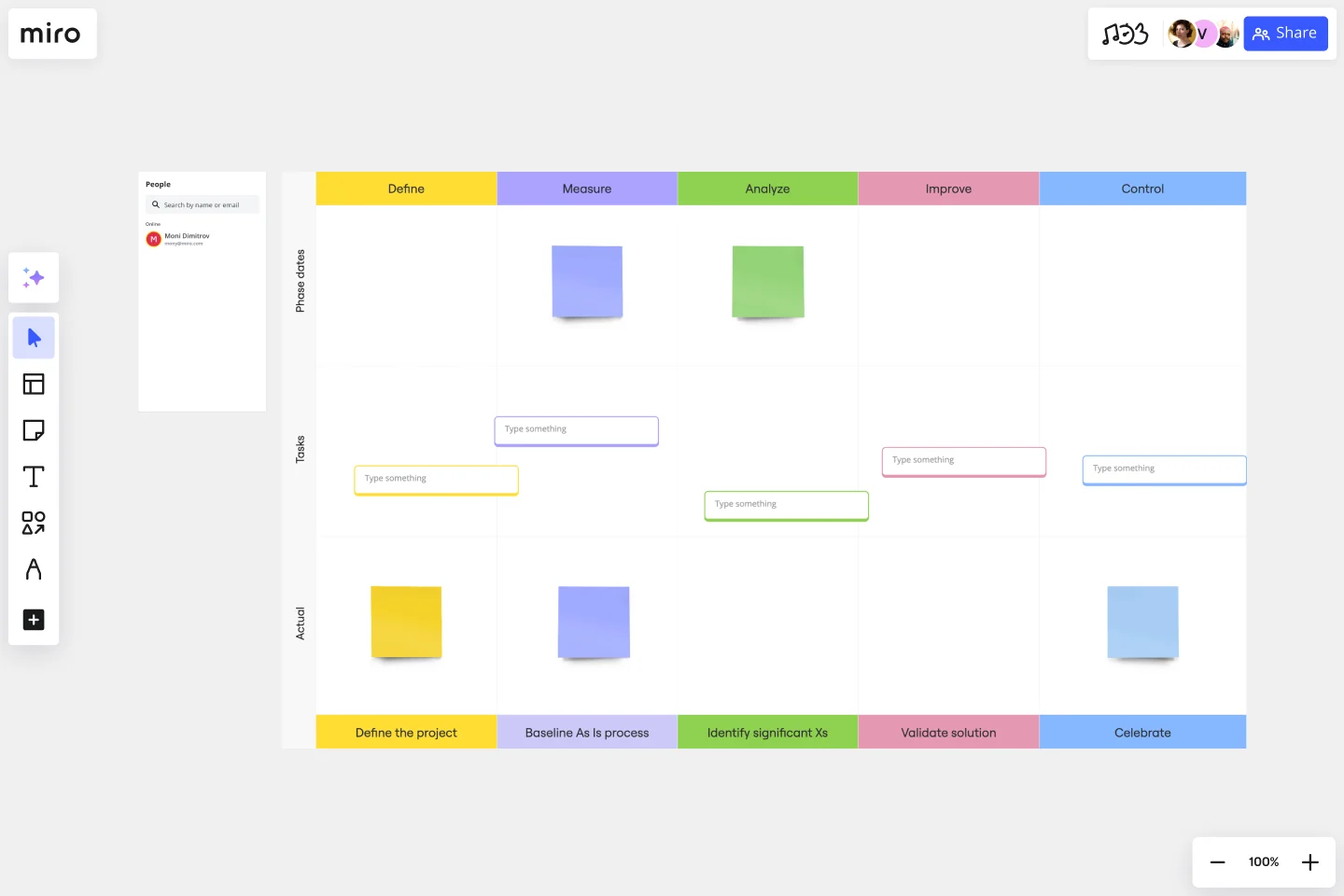
The template’s work plan is split into three rows, with key dates being at the top, tasks in the middle, and deliverables or outcomes at the bottom. Start by adding your tasks to the pre-made cards in the middle row. Double-click on a card to start typing, and expand it to add more details for each task. You can easily add more cards from the toolbar — or by duplicating existing ones.
3. Add your timeline
Tracking time is an important way to measure progress for any project. Use the sticky notes in the top row to fill out key dates and move them around as needed. You can also add more sticky notes by grabbing them from the toolbar or pressing N on your keyboard.
4. Add outcomes and deliverables
While you won’t know all your outcomes just yet, you can start identifying what your desired outputs and important deliverables are in the bottom row. Double-click on the sticky notes to start typing, and drag them around to adjust them as needed.
Of course, it’s normal for things to change throughout the course of a project (especially for large projects). Your work plan template cannot be all-encompassing – nor should it be. List as many goals, strategies, objectives, and tactics as possible and add dates for specific tasks, but don’t worry if you need to make adjustments later. Project management tools can be useful in helping you keep track of dates, tasks, and assignments.
What are the key components of a work plan?
A work plan has four components: goals, strategy, tactics, and deliverables. The goals are the ultimate aim of your project — what you want your team to accomplish. Your strategy is the big-picture approach to your project plan that you’ll implement to achieve your goals. Tactics are the smaller decisions, techniques, and action steps that you’ll employ to achieve your broader strategy. Deliverables are the specific, time-bound results you want to achieve from specific tasks — defined by your overall strategy.
Can I customize the look and feel of Miro’s work plan template?
Yes, Miro makes it easy for you to customize the work plan template according to your preferences. You can easily change the colors of your sticky notes, cards, and even the work plan itself. You can also customize font types and sizes and edit or remove any of the text boxes.
When to use a work plan?
You can use a work plan at the beginning of a project for strategic planning purposes, to scope the project, and continue to update the plan as the project progresses with actual data. Set a cadence of regular meetings so you can go over the plan, ensure you’re staying on track, and adjust as necessary. Work plans are especially helpful if you’re juggling many complex projects, managing multiple stakeholders, or working in tandem with cross-functional partners.
Get started with this template right now.
Working Backwards Template
Works best for:
Desk Research, Strategic Planning, Product Management
Find out how to use the Working Backwards template to plan, structure, and execute the launch of a new product. Using the template, you’ll figure out if the product is worth launching in the first place.
Work Breakdown Structure Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Mapping, Workflows
A work breakdown is a project management tool that lays out everything you must accomplish to complete a project. It organizes these tasks into multiple levels and displays each element graphically. Creating a work breakdown is a deliverable-based approach, meaning you’ll end up with a detailed project plan of the deliverables you must create to finish the job. Create a Work Breakdown Structure when you need to deconstruct your team's work into smaller, well-defined elements to make it more manageable.
Product Backlog Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Kanban Boards, Product Management
Development teams are often juggling many products at once. A product backlog is a project management tool that helps teams keep track of projects in flight as they build and iterate, so you can store everyone's ideas, plan epics, and prioritize tasks. The highest-priority tasks are at the top of the product backlog, so your team knows what to work on first. Product backlogs make it easier for teams to plan and allocate resources, but it also provides a single source of truth for everyone to know what development teams are working on.
Production Workflow Template
Works best for:
Agile Workflows, Agile Methodology, Project Management
Whether you’re producing a podcast, a marketing campaign, a TV show, or a piece of content, establishing a production workflow is crucial. A production workflow creates a visual guide to the different steps in a process. It can be used to train new team members or give a high-level overview to stakeholders. Although production workflows vary by team and business, they generally contain information about who the stakeholders are, how you brainstorm ideas, what your timeline looks like, and what resources you need to succeed.