Data Flow Diagram Template
Model processes and map data flows to improve internal processes.
Available on Enterprise, Business, Education plans.
About the Data Flow Diagram Template
The data flow diagram template is a visual tool you can use to improve your understanding of how data travels within a system — namely by visualizing the inputs, outputs, and the processes involved. Organizations use data flow diagrams (DFD) in many business activities, including depicting notation styles, physical requirements, and system automation.
We’ll walk you through how you can start creating a data flow diagram using Miro’s free and customizable DFD template.
How to use Miro’s data flow diagram template
To get started with Miro’s data flow diagram template, scroll to the top of this page and click on the blue “use template” button. That’ll open the template and allow you to start using Miro’s diagram maker. Once you’ve opened it, think about what type of system you’re trying to visualize — whether it’s a business process, data flow within a software application, or something else. When you’re ready, here are a few more steps to make the most of the data flow diagram template.
1. Identify inputs and outputs
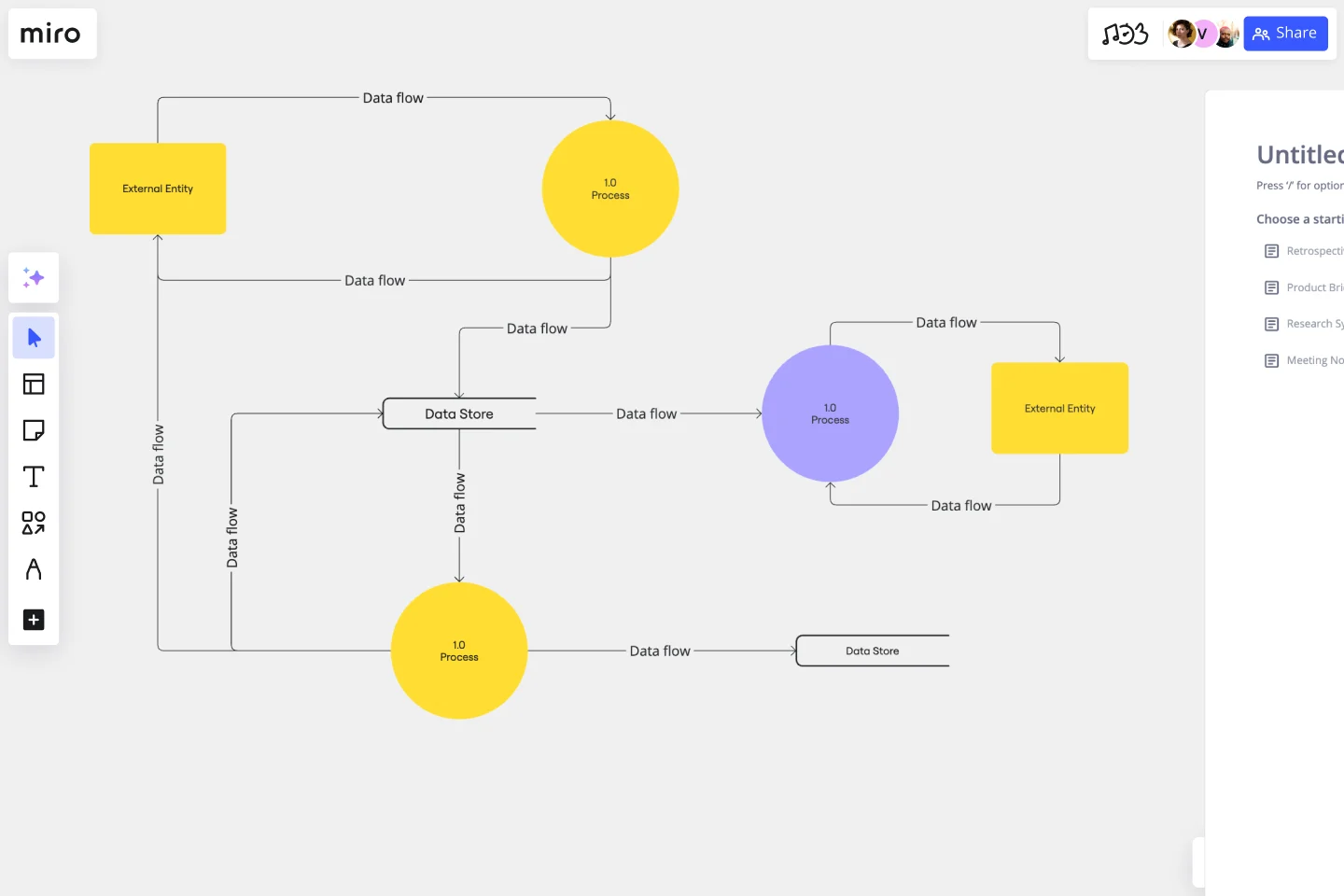
Each process you aim to map out should have at least one input and one output. This helps make sure that your DFD template is complete and has no loose ends. Look for the two blue, rounded rectangles on the left and right of the DFD template marked “external entity,” then edit the text boxes within them to label where the data is entering the system from and where it’ll go. To add more input and output sources, right-click on the rectangle and choose “Duplicate.”
2. Identify processes
On the data flow diagram template, the three circles labeled “Process” are for you to identify the activities or functions that manipulate data in some way. Edit the text boxes to add your system’s processes, and easily delete or duplicate these circles as needed.
3. Identify data stores
There are two symbols on the template labeled “data store.” As its name implies, it refers to where the system stores its data. Double-click on the text boxes to edit them and replace the text with how you want to label your data stores. Duplicate these symbols as needed, and click and drag them if you’d like to adjust their position on the diagram.
4. Label data flows
Last but not least, don’t forget to visualize the flow of data. The template comes with arrows connecting inputs, outputs, processes, and data stores. Edit the text along these arrows to identify the type of data that’s traveling, and click and drag them to adjust the direction of flow appropriately.
Is Miro’s data flow diagram template free?
Yes, Miro’s data flow diagram template is free and fully customizable, so you can make it your own. Just click on the blue “use template” button on this page to get started.
Who is Miro’s data flow diagram template for?
Miro’s data flow diagram template is for any team involved in system development, analysis, optimization, and collaboration — including data analysts, software development teams, growth teams, and product teams.
What’s the difference between a data flow diagram and a flowchart?
A data flow diagram is your guide to understanding the nitty-gritty of how information travels within a system — such as databases, software applications, and business processes. While a flowchart also visualizes flows, it isn’t limited to representing data. Flowcharts are versatile maps that outline processes, decisions, and actions much more broadly. Miro's free data flow diagram template is specially crafted to visualize the intricacies of data flow within complex systems.
Get started with this template right now. Available on Enterprise, Business, Education plans.
UML Diagram Template
Works best for:
Diagrams, Software Development
Originally used as a modeling language in software engineering, UML has become a popular approach to application structures and documenting software. UML stands for Unified Modeling Language, and you can use it to model business processes and workflows. Like flowcharts, UML diagrams can provide your organization with a standardized method of mapping out step-by-step processes. They allow your team to easily view the relationships between systems and tasks. UML diagrams are an effective tool that can help you bring new employees up to speed, create documentation, organize your workplace and team, and streamline your projects.
Swimlane Diagram Template
Works best for:
Flowcharts, Diagrams, Workflows
A swimlane diagram shows you which stakeholders are responsible for each area of your critical processes. You can use it to understand current processes or plan new ones.
Decision Tree Template
Works best for:
Decision Making, Mind Mapping, Diagrams
Making difficult decisions gets easier when you can look clearly at your choices and visualize the outcomes. That’s just what a decision tree will help you do, empowering you to invest your time and money with confidence. A decision tree is a flowchart that looks just how you’d imagine—with “branches” that represent your available choices. It provides a stylized way to play out a series of decisions and see where they lead before you commit your real-world resources, which is especially valuable for startups and smaller companies.