About the SAFe ROAM Board
A SAFe ROAM Board is a framework for making risks visible. It gives you and your team a shared space to notice and highlight risks — and to determine which risks to Resolve, Own, Accept or Mitigate.
Use this template to assess the likelihood and impact of risks, and decide which risks are low priority versus high priority.
The underlying principles of SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) are:
Drive cost-effective solutions
Apply systems thinking
Assume that things will change; protect options
Build incrementally with fast integrated learning cycles
Base milestones on evaluating working systems
Visualize and limit works in progress, reduce batch sizes, manage queue lengths
What is a SAFe ROAM Board?
A SAFe ROAM Board is a useful SAFe tool that allows you and your team to highlight risks so that you can take action. After someone identifies and records a risk, you have to decide what to do next. For each risk you come across, you can:
Avoid it and take a different approach
Reduce the likelihood that it’ll happen
Share the risk by bringing in vendor expertise
Accept the risk (but keep in mind, this doesn’t mean you ignore it)
Mitigate the risk and take action to reduce its impact
This framework aims to help you Resolve, Own, Accept, or Mitigate risks.
Resolved risks: your team agrees that this risk is no longer an issue and everyone can move on
Owned risks: if a risk isn’t immediately solved, a team member may take ownership of the task to resolve later (follow up to plan mitigation or work on executing any further action that should be taken)
Accepted risks: some risks can’t be reasonably dealt with, so teams should fully understand why before accepting these risks
Mitigated risks: a mitigation plan can reduce the likelihood or impact of these risks
It’s important to keep your ROAM Board updated so your team is aligned across each level of risk, and aware of how risks are being handled. If your team uses Jira, import Jira cards directly onto your SAFe Roam Board.
Create your own SAFe ROAM Board
Making your own SAFe ROAM Boards is easy with Miro's template. Get started by selecting the SAFe ROAM Board template, then take the following steps to make one of your own:
During PI Planning, add risks to the Program Risks section. Remember that the number of sticky notes with identified risks may grow or shrink as your team decides on a mitigation strategy during the planning process.
After the final plan review, move all risks to the ROAM Board. Allocate each risk to the relevant category of ROAM: Resolved, Owned, Accepted, Mitigated.
Vote as a team to decide which risks are worth prioritizing. Agile coaches can run voting sessions to decide which risks should be considered high priority. A minimum of three votes is needed to consider a risk in the running as a high priority.
Review and adjust risks as needed. Risk profiles can change as plans and follow-up steps to action. Make sure a member of your team adjusts and updates the board during the weekly or biweekly PO (Product Owner) Sync.
When to use SAFe ROAM Boards
ROAM Boards are used as a PI Planning tool during PI Planning sessions to identify any obstacles to achieving team goals.
Risk and uncertainty are bound to impact any project in some way. Instead of relying on a classic risk management plan or risk log, an Agile approach (such as creating more user stories to add to a backlog) can lower the chances of unpredictability and surprise.
The ROAM method can also help relieve the Agile Release Train (the teams and stakeholders needed to implement, test, deploy, and release software incrementally) of any ambiguity.
FAQ about the SAFe ROAM Board
What is a ROAM board?
A ROAM board is a framework for highlighting the likelihood and impact of risks, in order to decide which risks are low priority versus high priority. This framework aims to help you Resolve, Own, Accept, or Mitigate risks and increases the visibility of risk management to everyone on the team, which ensures that potential risks are not overlooked or ignored.
What does SAFe stand for in agile?
SAFe stands for Scaled Agile Framework and defines a set of roles, responsibilities, and guiding principles for everyone involved in a SAFe project or working at an enterprise level that follows agile practices.
When is the ROAM technique used to categorize program risks?
The ROAM framework is used when teams need to identify and manage risks and, as an Agile technique, is often followed by those involved in SAFe project management. Using a ROAM board helps keep everyone aligned across each level of risk and maintains awareness of how all identified risks are being handled.

Miro
The AI Innovation Workspace
Miro brings teams and AI together to plan, co-create, and build the next big thing, faster. Miro empowers 100M+ product managers, designers, engineers, and more, to flow from early discovery through final delivery on a shared, AI-first canvas. By embedding AI where teamwork happens, Miro breaks down silos, improves alignment, and accelerates innovation. With the canvas as the prompt, Miro's collaborative AI workflows keep teams in the flow of work, scale shifts in ways of working, and drive organization-wide transformation.
Categories
Similar templates

Agile Transformation Roadmap
An Agile transformation roadmap can help you, your team, and your organization transition from rigid compliance-heavy methods to the more flexible Agile way of doing things incrementally. From requirements to integrations to security, you can map out your organization's moving parts as “swim lanes” that you can then update regularly. Use your roadmap as a way to tell the story of how you see your product growing over a period of time. Get buy-in without overselling and keep your roadmap simple, viable and measurable. By using an Agile transformation roadmap, you can avoid getting bogged down in details and instead invest in big-picture strategic thinking.
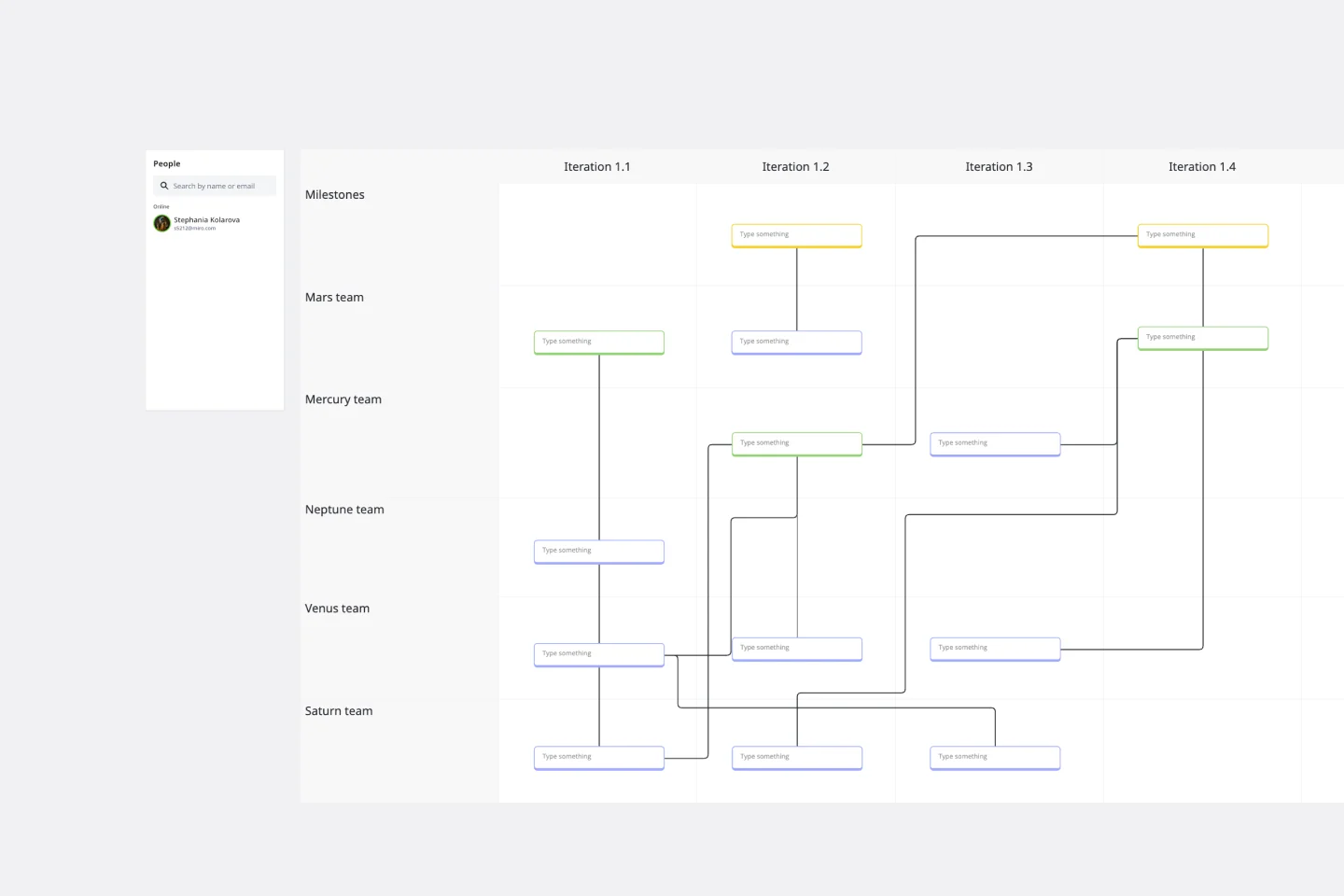
SAFe Program Board
Many organizations use the Agile model, but even companies that don’t rigorously adhere to all Agile standards have adopted Agile tools and methods like Program Increment (PI) Planning. Even if you’re not participating in a formal PI session, a program board can be a great way to establish communication across teams and stakeholders, align development objectives with business goals, clarify dependencies, and foster cross-functional collaboration. The board provides much-needed structure to planning sessions, yet is adaptable enough to accommodate brainstorming and alignment meetings.
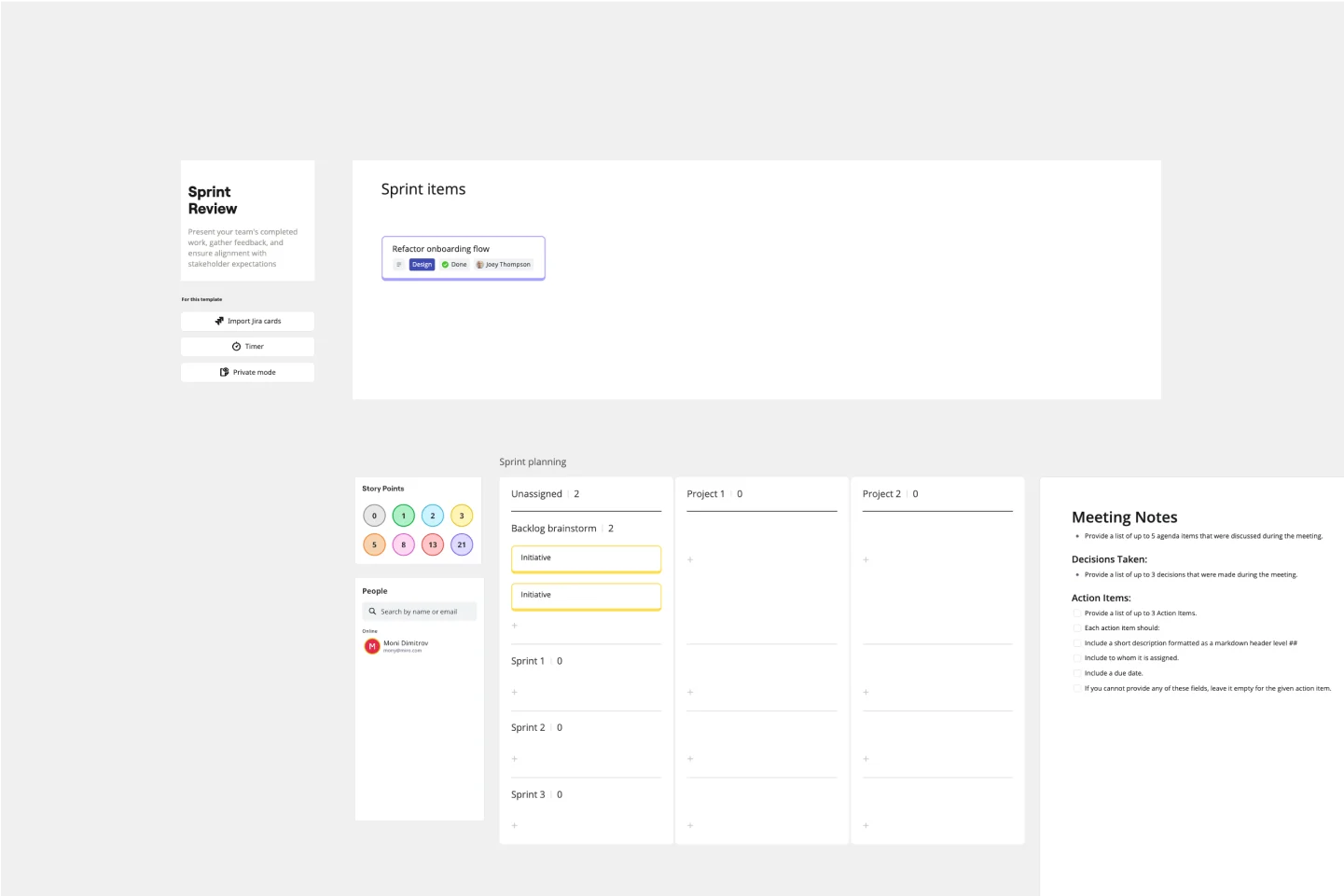
Sprint Review Template
The Sprint Review Template is a vital tool in Agile project management that enhances communication between team members and stakeholders by providing a clear format for presenting the sprint's accomplishments and challenges. It encourages active participation and feedback from all attendees, leading to more informed decision-making and continuous improvement. In essence, it's a catalyst for meaningful dialogue and collaborative growth.

Agile Transformation Roadmap
An Agile transformation roadmap can help you, your team, and your organization transition from rigid compliance-heavy methods to the more flexible Agile way of doing things incrementally. From requirements to integrations to security, you can map out your organization's moving parts as “swim lanes” that you can then update regularly. Use your roadmap as a way to tell the story of how you see your product growing over a period of time. Get buy-in without overselling and keep your roadmap simple, viable and measurable. By using an Agile transformation roadmap, you can avoid getting bogged down in details and instead invest in big-picture strategic thinking.

SAFe Program Board
Many organizations use the Agile model, but even companies that don’t rigorously adhere to all Agile standards have adopted Agile tools and methods like Program Increment (PI) Planning. Even if you’re not participating in a formal PI session, a program board can be a great way to establish communication across teams and stakeholders, align development objectives with business goals, clarify dependencies, and foster cross-functional collaboration. The board provides much-needed structure to planning sessions, yet is adaptable enough to accommodate brainstorming and alignment meetings.

Sprint Review Template
The Sprint Review Template is a vital tool in Agile project management that enhances communication between team members and stakeholders by providing a clear format for presenting the sprint's accomplishments and challenges. It encourages active participation and feedback from all attendees, leading to more informed decision-making and continuous improvement. In essence, it's a catalyst for meaningful dialogue and collaborative growth.