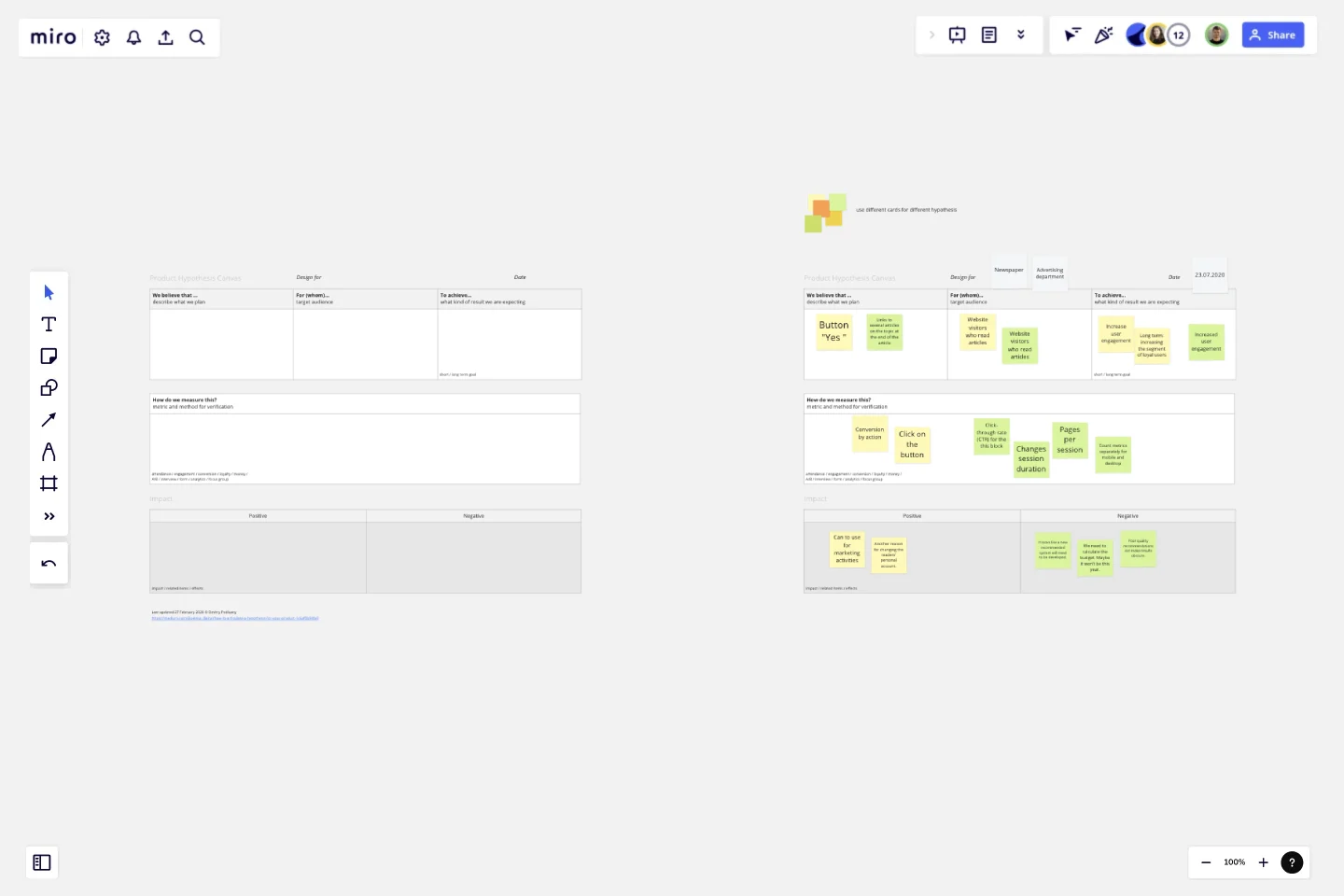
Product Hypothesis Canvas
We are increasingly shifting from projects centered on the demands of customers or users to projects focused on product hypotheses.
We are increasingly shifting from projects centered on the demands of customers or users to projects focused on product hypotheses. There are several reasons for this.
On the one hand, we are expected to implement new functions within increasingly shorter deadlines. That’s because the competition is getting fiercer, and the world, thanks to modern technology, keeps speeding up and getting more complex.
On the other hand, having more diverse groups of users means facing more diverse needs. We are moving at full speed towards an entirely customizable world. And this creates an even greater demand for instantaneous product adjustments.
If “demands” require implementation, then “hypotheses,” above all, need to be tested. But before that, the hypotheses must be coherently articulated. Which is not always as easy as we would have wanted.
We believe that the more coherent the hypothesis, the more fruitful testing it will be. Testing in this sense covers not just the verification of the actual hypothesis, but also any possible insights that may be gathered in the process. To structure and simplify the process of articulating your hypothesis, we have singled out the following questions, which you can answer sequentially.
The Product Hypothesis Canvas helps you create more effective hypotheses. Keep in mind that the canvas does not do the work for you; it simply helps you focus on the task at hand and reach a more effective solution.
The steps for filling out the Product Hypothesis Canvas
We believe that…
Here, we describe what we plan to develop.
2. For (whom)…
In this block, we define our target audience and, if required, evaluate its role in our project.
This step is very important, as it will later help us rank our hypotheses by their relevance to our project. Sometimes, project team members become utterly seduced by an interesting idea, and end up forgetting that it is only applicable to a few isolated cases.
In fact, if the author is unable to coherently explain whom their hypothesis is going to benefit, it’s very likely that they are just indulging in random guesswork. That is like when a pool player breaks with a powerful strike, hoping to pocket a ball at random. In the same way, product managers and designers generate hypotheses with no connection to the users, hoping that at least someone is going to be interested. Be really careful with such hypotheses; it may be worth the time to think about them in greater detail.
3. To achieve…
It is also important to determine what kind of result we are expecting from our experiment. Moreover, the result should preferably be measurable in specific terms. Don’t write, “We must do better!” It’s better to express your expectations like, “We must improve [product] by 5%.”
Depending on the hypothesis, we may have different expectations for short-term and long-term results. Many people prefer to focus on short-term results and avoid working with hypotheses that have more far-reaching goals. But when we create our hypothesis, we must be aware of how long it will take to test it: a day, a week, a month, or maybe even longer. With that in mind, we will later be able to plan a backlog of our experiment.
4. How do we measure this?
The ability to measure the results is the key parameter for testing product hypotheses. While we already mentioned what we are going to measure in the previous step, here we describe the kinds of tools we are going to use for this. What signals will indicate that the opportunity we have created is impactful? Which key performance indicators (qualitative or quantitative) are we going to measure to prove our experiment was successful?
5. Impact, positive or negative
We have introduced this block in case we want to approach our hypothesis as something beyond a single objective. Filling it in is not mandatory.
In some cases, the introduction of a certain function has a negative impact on other parameters within the system. For example, we add an extensive, informative presentation
to our home page, hoping to increase user engagement. However, the presentation impacts the page’s loading speed, which, contrary to our intent, increases the bounce rate, potentially reducing engagement. In this specific case, the higher bounce rate is probably not caused by the functionality itself but by its bulkiness and poor implementation.
Get started with this template right now.
Kano Model Template
Works best for:
Desk Research, Product Management, Prioritization
When it comes down to it, a product’s success is determined by the features it offers and the satisfaction it gives to customers. So which features matter most? The Kano model will help you decide. It’s a simple, powerful method for helping you prioritize all your features — by comparing how much satisfaction a feature will deliver to what it will cost to implement. This template lets you easily create a standard Kano model, with two axes (satisfaction and functionality) creating a quadrant with four values: attractive, performance, indifferent, and must-be.
Impact/Effort Matrix Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Strategic Planning, Prioritization
Growing organizations have countless to-do’s and only so many hours in a day (or weeks before a big launch) to get them done. That’s where an impact effort matrix comes in. It gives you a quick visual guide to help prioritize your tasks and know exactly what’s worth doing. Using our template, you can create a matrix that organizes your activities into four main categories: quick wins that are low effort, effort-intensive projects that provide long-term returns, fill-ins that are low effort but low value, and time-wasters.
All-in-one PI Planning
Works best for:
Agile
The All-in-one PI Planning template streamlines the SAFe Program Increment (PI) Planning process by providing a comprehensive framework for teams to collaboratively plan and align on objectives and dependencies. It integrates essential elements such as PI Objectives, Team Breakouts, and Program Board, enabling teams to visualize, prioritize, and coordinate work effectively. This template empowers Agile Release Trains to deliver value predictably and efficiently, driving alignment and synchronization across the organization.
Taco Tuesday Retrospective
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Retrospectives, Meetings
The Taco Tuesday Retrospective template offers a fun and informal approach to retrospectives, perfect for fostering team camaraderie. It provides elements for reflecting on past iterations over a casual taco-themed gathering. This template enables teams to relax, share insights, and brainstorm ideas in a laid-back atmosphere. By promoting social interaction and creativity, the Taco Tuesday Retrospective empowers teams to strengthen relationships, boost morale, and drive continuous improvement effectively.
Ansoff Matrix Template
Works best for:
Leadership, Operations, Strategic Planning
Keep growing. Keep scaling. Keep finding those new opportunities in new markets—and creative new ways to reach customers there. Sound like your approach? Then this template might be a great fit. An Ansoff Matrix (aka, a product or market expansion grid) is broken into four potential growth strategies: Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, and Diversification. When you go through each section with your team, you’ll get a clear view of your options going forward and the potential risks and rewards of each.
One Page Product Strategy
Works best for:
Product Management, Planning
The One Page Product Strategy template condenses complex product strategies into concise, actionable plans. By providing a structured framework for outlining goals, target markets, and key initiatives, this template enables product teams to align on strategic objectives efficiently. With sections for defining value propositions, competitive differentiators, and success metrics, it facilitates strategic decision-making and execution. This template serves as a roadmap for driving product development efforts and achieving business objectives effectively.