
Table of contents
Table of contents
What is a prototype?

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
- What a prototype is: a working, evolving model to test ideas.
- How Miro supports prototyping: tools for low-, mid-, and high-fidelity prototypes.
- Benefits of AI-powered prototyping in Miro: instant generation, automatic flows, and rapid iteration.
- How Miro facilitates collaboration: real-time co-creation, commenting, and centralized project management.
- Role of prototyping: accelerates design workflows, improves communication, enables early user testing.
- Key Miro prototyping features: interactive preview, connector lines, AI generation, component library.
What is a prototype? Understanding the heart of product design
When it comes to creating a new product, there's a lot more to it than just brainstorming and sketching. Enter the world of prototypes, a critical step in bringing a product to life. Prototypes are more than just models; they're the tangible manifestations of an idea. They allow you to test concepts, identify problems, and refine the product before it goes into full production.
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Prototypes: More than just mockups
At its core, a prototype is a working model of a product. It's not a final version but rather an evolving version designed to help you understand how the product will work in the real world. Think of it as a tool to communicate your vision to others—whether that's stakeholders, developers, or other designers.
Prototypes come in all shapes and sizes. Some are basic, low-fidelity models made of paper or foam, while others are high-fidelity digital versions with interactive elements. The type of prototype you use depends on your goals and the stage of development you're in. Early on, you might use simple sketches or wireframes. As you get closer to production, your prototypes might include detailed graphics, user interfaces, and functional components.
The role of prototypes in Design Thinking
Prototypes play a crucial role in design thinking, emphasizing empathy, creativity, and iteration to solve complex problems. In design thinking, prototyping is used to explore and validate ideas in a tangible way. It allows teams to quickly test concepts, learn from feedback, and iterate based on real-world insights.
The beauty of prototyping in design thinking is its flexibility. You can start with low-fidelity prototypes to explore a wide range of ideas and then gradually increase the fidelity as you refine the concept. This iterative process helps design teams stay open to new ideas and pivot when necessary, leading to more innovative and user-centric solutions.
Prototyping also fosters collaboration within design thinking. Since prototypes are visual and interactive, they facilitate communication among cross-functional teams. This shared understanding helps align everyone toward a common goal, reducing miscommunication and ensuring a smoother development process.
The role of prototypes in product development
In product development, prototypes serve as a bridge between the initial idea and the final product. Before committing to full-scale production, they are essential for testing feasibility, usability, and functionality. Product teams can identify design flaws, technical issues, and user experience problems early on by creating prototypes, saving time and resources.
Prototypes in product development also serve as a tool for stakeholder engagement. They allow you to present your concept in a way that is easy to understand, increasing buy-in from decision-makers. This is especially important when seeking funding or approval for further development.
Additionally, prototypes are crucial for user testing in product development. They provide a realistic environment for gathering feedback from real users, allowing you to understand their needs and preferences. This feedback loop is invaluable for refining the product and meeting customer expectations.
The different types of prototypes and when to use them
Prototypes can be divided into several categories based on their fidelity and purpose. Understanding these types and knowing when to use each can help you choose the right approach for your project.
Low-Fidelity Prototypes

These are simple, often hand-drawn models focusing on basic structure and layout. They're great for early-stage brainstorming, concept validation, and quick iteration. Use them when you need to explore a wide range of ideas without investing too much time or resources. Try our low-fidelity prototype template.
High-Fidelity Prototypes
These are more detailed and closely resemble the final product. They often include interactive elements, detailed graphics, and realistic user interfaces. Use them when you need to simulate the user experience, test functionality, or present to stakeholders.
Functional Prototypes
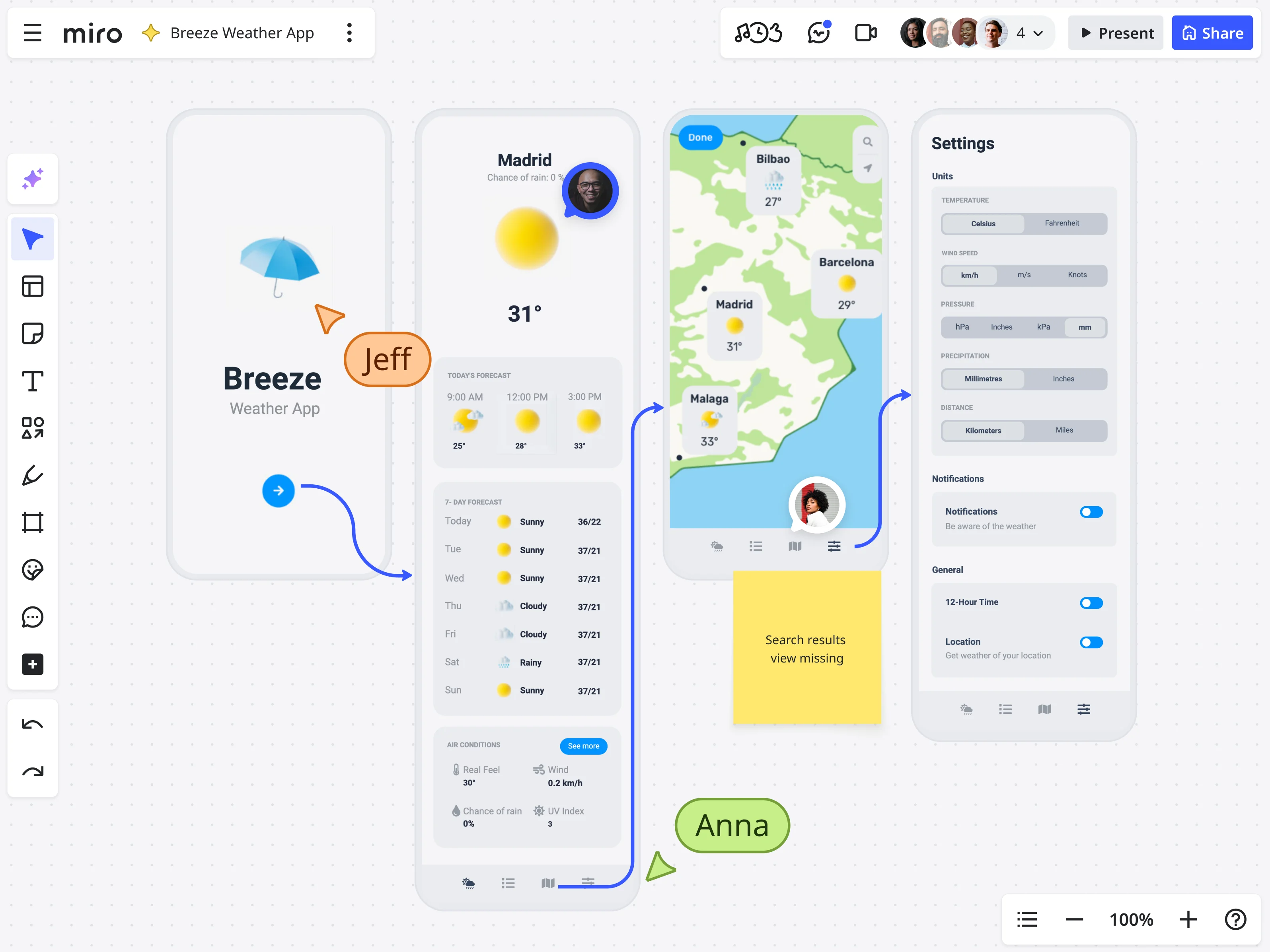
These prototypes focus on the working aspects of the product. They're used to test functionality and identify technical issues. Use them when you need to ensure the product works as intended and is technically feasible.
Interactive Prototypes

These are digital models that allow users to interact with the product, simulating the user experience. They're valuable for usability testing and gathering feedback. Use them when you want to understand how users interact with your product and identify areas for improvement.
Prototyping in action: The process
The prototyping process typically involves several stages, each with its own objectives and outcomes. Here's a high-level overview:
- Concept development: This is where you brainstorm ideas and create low-fidelity prototypes to explore different concepts. The goal is to identify a direction for your product.
- Design and development: Once you've settled on a concept, you start creating more detailed prototypes. This stage involves refining the design, adding interactive elements, and testing functionality.
- User testing: At this stage, you gather feedback from real users. This is where interactive prototypes shine. You can observe how users interact with the product and identify areas for improvement.
- Iteration and refinement: Based on user feedback, you make adjustments to the prototype. This stage is iterative, meaning you might go through several rounds of testing and refinement before finalizing the design.
Miro: The go-to tool for prototyping and product development
When it comes to prototyping, having the right tools can make all the difference. Miro is a platform designed to streamline the prototyping process and improve collaboration. With Miro, you can create low-fidelity sketches, high-fidelity wireframes, and interactive prototypes—all in one place.
Now, with the introduction of our new AI-powered prototyping features, we're dramatically accelerating this process. You can instantly generate initial prototype concepts, build interactive flows with ease, and rapidly iterate on designs using the power of AI, seamlessly integrated into your familiar collaborative workspace. This means you can move from brainstormed idea to a testable, interactive prototype faster than ever, empowering your whole team to contribute and align on the product vision sooner.
If you are working on a new app, a physical product, or a website, Miro gives you all the necessary features to create prototypes that resonate with your team and stakeholders. With its flexibility and collaborative capabilities, Miro is the perfect tool for product development, giving you confidence to move from concept to reality.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 22, 2025