Table of contents
Table of contents
The ultimate Scrumban guide for Agile teams

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
- What Scrumban is and how it combines Scrum and Kanban
- Key principles: workflow visualization, limiting WIP, pull-based tasks
- How Scrumban boards are designed and used to track tasks
- Differences between Scrumban and traditional Scrum (on-demand planning vs. fixed sprints)
- How metrics like cycle time and cumulative flow diagrams support continuous improvement
- Practical steps for implementing Scrumban in project management
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Scrumban offers the best of both Kanban and Scrum. Think your team could benefit from both methodologies? Our detailed guide covers everything you need to opt for the best way of working. Let's dive in.
What is Scrumban?
Scrumban is a project management methodology that combines the structured approach of Scrum with the flexibility and visualization of Kanban. Originally designed to help teams transition from Scrum to Kanban, Scrumban has since evolved into its own hybrid framework, making it a powerful tool for teams that need both structure and adaptability.
By blending these two popular methodologies, Scrumban helps teams improve their workflows, visualize their tasks, and continuously optimize their processes. The result? A more agile, responsive way of working that suits teams with shifting priorities or those looking for a less rigid framework.
Benefits of using Scrumban
So, why is Scrumban so important? We've highlighted a few of the key benefits:
Flexibility and adaptability
Unlike Scrum, which is often tied to fixed sprints, Scrumban allows teams to adapt their workflow as needed. There’s no need to wait for the end of a sprint to make changes—this makes Scrumban ideal for teams that deal with unpredictable work or fast-changing environments.
Improved workflow efficiency
Scrumban helps teams visualize their processes and set clear work-in-progress (WIP) limits. By doing so, teams can reduce bottlenecks and focus on completing tasks rather than overloading themselves with too many at once. This leads to faster turnaround times and higher-quality outcomes.
Enhanced team collaboration
By merging elements of Scrum and Kanban, Scrumban encourages regular communication and collaboration. Teams can still hold daily stand-ups, but they do so within a more flexible framework that reduces the pressure of strict deadlines. This is particularly helpful for cross-functional teams or teams spread across different locations.
Continuous improvement
Scrumban promotes continuous improvement, or Kaizen, by allowing teams to adjust their processes on the fly. Teams are encouraged to reflect on their performance regularly, ensuring that their workflows evolve over time and are always optimized for the current situation.
How Scrumban combines Scrum and Kanban
As its name implies, Scruman draws qualities from both Scrum and Kanban frameworks. Here's a closer look at how:
Scrum elements in Scrumban
While Scrumban introduces more flexibility than traditional Scrum, it retains many of Scrum’s core elements. Teams can still use roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner to ensure accountability and leadership within the project. Sprint planning, too, is still possible, although it may not follow the rigid time-boxed format of standard Scrum.
For anyone beginning with Scrum, our Scrum templates offer a practical toolkit for organizing workflows and ensuring smooth project management.
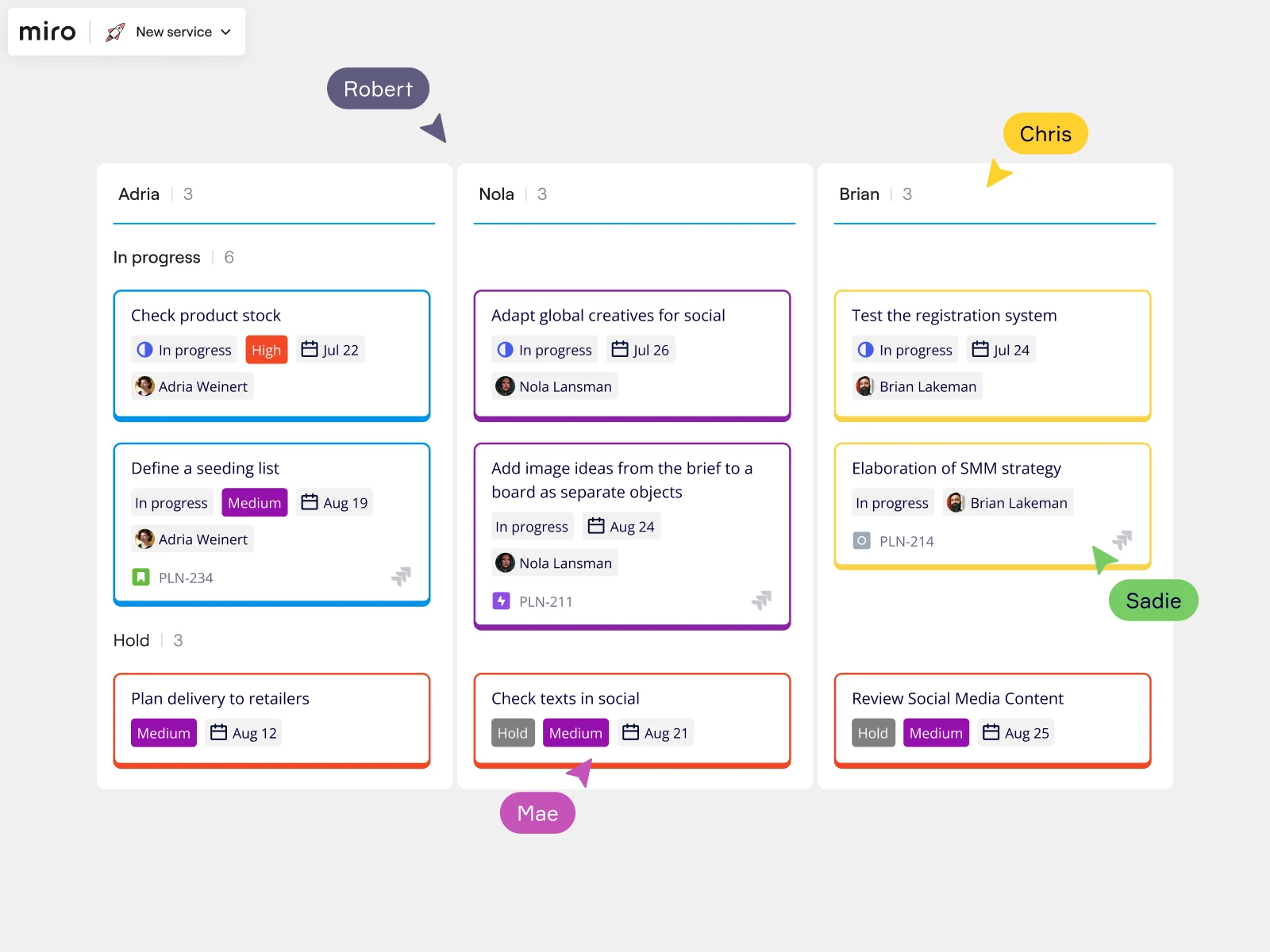
Kanban elements in Scrumban
Kanban’s visual approach is central to Scrumban. By using boards, columns, and cards to represent tasks, teams can track their progress in real-time. Work-in-progress (WIP) limits are also borrowed from Kanban, ensuring that teams don’t take on too much work at once. This helps maintain focus and improves overall productivity.

Scrumban vs. Scrum vs. Kanban
So what exactly are the differences between Scrumban, Scrum, and Kanban? Let's take a look:
Scrumban vs. Scrum
The main difference between Scrumban and Scrum is flexibility. In Scrum, work is planned out for each sprint, meaning changes are often deferred until the next sprint cycle. In contrast, Scrumban allows for more fluidity, meaning changes can be made as soon as new information becomes available. For teams with less predictable workloads, Scrumban may be the better option.
Scrumban vs. Kanban
While Scrumban incorporates many elements of Kanban, such as visual task management and WIP limits, it retains some of the structured planning aspects of Scrum. Kanban alone is more focused on flow and continuous delivery, whereas Scrumban provides a middle ground, making it suitable for teams that want the best of both worlds.
Key components of the Scrumban methodology
You can always tell Scrumban by the following principles:
Work visualization
Scrumban emphasizes visualizing work, typically through a Kanban board. Each column represents a stage of the process, and tasks move through the stages as they’re completed. This visual clarity helps teams understand where work is piling up and allows them to adjust accordingly.
Limiting Work in Progress (WIP)
One of Scrumban’s most valuable principles is limiting WIP. By setting strict limits on how many tasks can be in progress at once, teams avoid overcommitting and are able to focus on completing tasks more quickly and efficiently. This leads to a more streamlined workflow and prevents bottlenecks.
Pull-based work system
Scrumban employs a pull-based system, meaning tasks are “pulled” into the workflow only when there’s capacity to handle them. This ensures that no one is overloaded with work, and it keeps the process moving at a sustainable pace. By limiting the amount of work in progress, teams can maintain steady productivity without burnout.
Process improvement through Kaizen
In Scrumban, continuous improvement (Kaizen) is key. Teams regularly review their performance and adjust their workflows to improve efficiency and quality. This iterative approach means the process is always evolving, ensuring that it stays aligned with team goals and external factors.
Scrumban practices in action
Let's look at a few examples of Scrumban in action:
Sprint-less planning
Unlike Scrum, where sprint planning is fixed, Scrumban allows for on-demand planning. Teams can plan as needed, making it easier to adapt to changing requirements. This makes Scrumban particularly useful for teams that need to balance longer-term planning with the ability to react quickly to new information.
Metrics and performance measurement
To ensure continuous improvement, Scrumban uses metrics like cycle time (how long it takes to complete a task) and lead time (how long it takes from task assignment to completion). Cumulative flow diagrams (CFDs) are also useful for tracking how work is progressing through the stages of a Kanban board.
Managing workflows and backlogs
With Scrumban, managing your workflow becomes more dynamic. Tasks are pulled into the process only when there’s capacity to handle them, ensuring that teams aren’t overwhelmed. Regular backlog grooming sessions ensure that tasks are always prioritized and relevant to current needs.
Who should use Scrumban?
So, what teams are best suited to Scrumban? We've highlighted a few tips:
Best use cases for Scrumban
Scrumban is ideal for teams that need the structure of Scrum but want the flexibility of Kanban. It’s particularly useful for teams transitioning between methodologies or for those dealing with unpredictable workloads. Teams in maintenance, support, or operations, where priorities can shift quickly, often find Scrumban to be the perfect fit.
Industries and teams that benefit most
Scrumban works well in industries where flexibility is key, such as software development, marketing, or any field that requires regular adjustments to workflows. Cross-functional teams, or teams working with external stakeholders, can also benefit from Scrumban’s adaptable structure.
Common misconceptions about Scrumban
When deciding which framework your team needs, it's also worth keeping in mind a few misconceptions about Scrumban:
Misunderstanding the blend of Scrum and Kanban
One common misconception is that Scrumban is simply a stepping stone between Scrum and Kanban. While it can serve that purpose, it’s a fully-fledged methodology on its own, offering distinct advantages to teams that need both structure and flexibility.
The myth of 'no planning' in Scrumban
Given its flexible style, it's easy to assume that Scrumban lacks planning. In reality, Scrumban involves continuous planning, allowing teams to adjust their priorities as needed without sacrificing the benefits of long-term thinking.
Is Scrumban a temporary framework?
Scrumban is often seen as a temporary framework for teams moving from Scrum to Kanban, but it can be a long-term solution. Many teams find that it strikes the right balance between the structure of Scrum and the flexibility of Kanban, making it a sustainable method for continuous improvement.
How to implement Scrumban in your organization
Implementing Scrumban can be a game-changer for teams looking for both flexibility and structure. Here’s a clear approach to help you get started:
1. Assess your current workflow
Look at your team’s current workflow and identify areas needing flexibility or structure. This assessment helps you see where Scrumban can make the biggest difference.
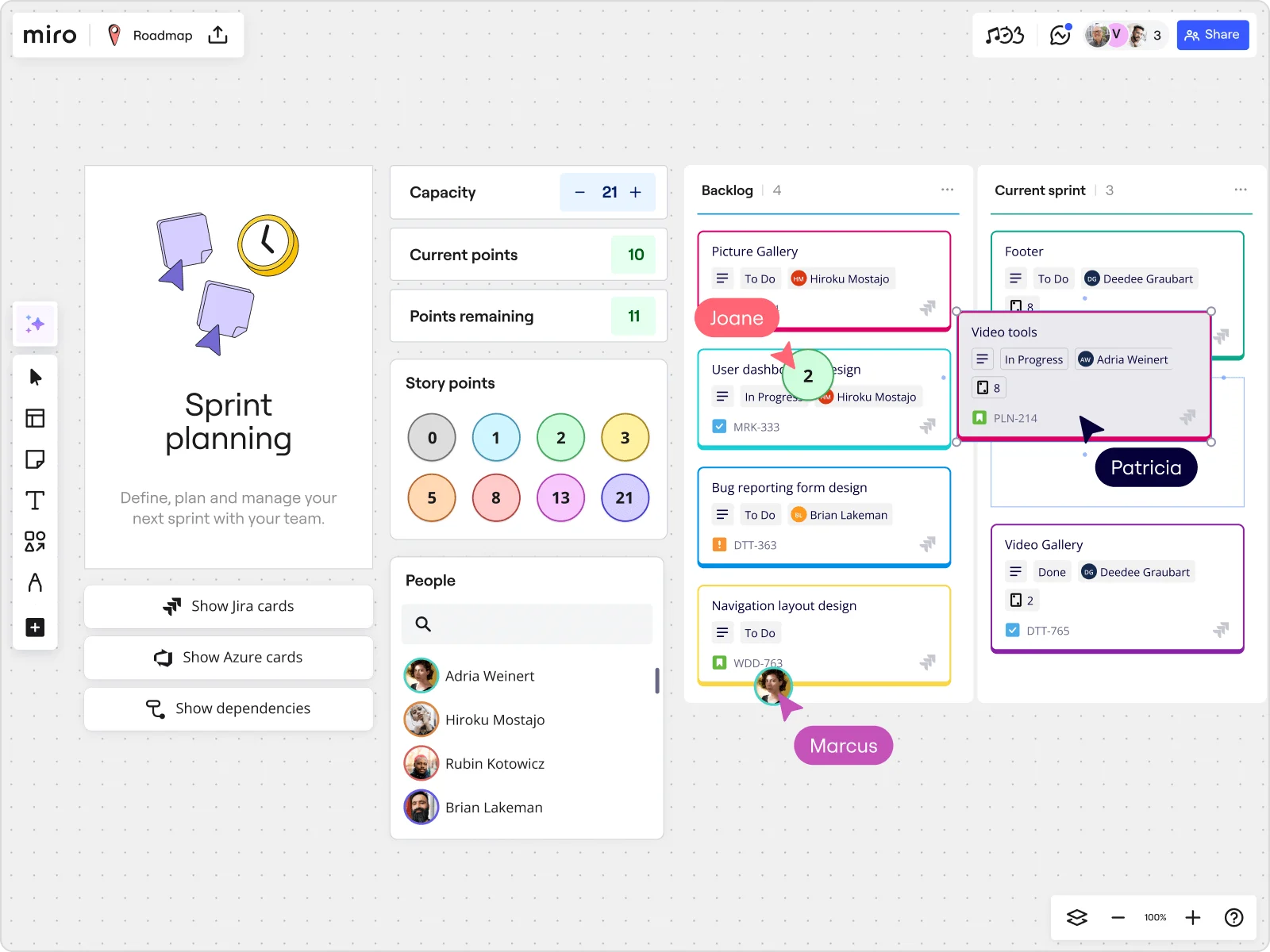
2. Set up a Kanban board
Create a simple Kanban board to visualize each step in your workflow. Use columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done” so everyone can easily track work at a glance.
3. Define work-in-progress (WIP) limits
Establish WIP limits to avoid task overload. Limiting tasks in each stage keeps the team focused and reduces unfinished work.
4. Hold regular retrospectives
Run regular retrospectives to review what’s working and what could be improved. This gives everyone a chance to discuss challenges and fine-tune the process.
5. Adapt and evolve
Keep Scrumban flexible by making small tweaks as your team grows. Adjust WIP limits, add or change steps, and keep evolving to meet your team’s needs.
Tools and software for Scrumban
To make Scrumban even easier, consider using digital tools like Miro, Jira, or Trello to manage your boards and workflows. These platforms allow teams to collaborate in real time, ensuring that everyone is always up to speed on the latest updates.
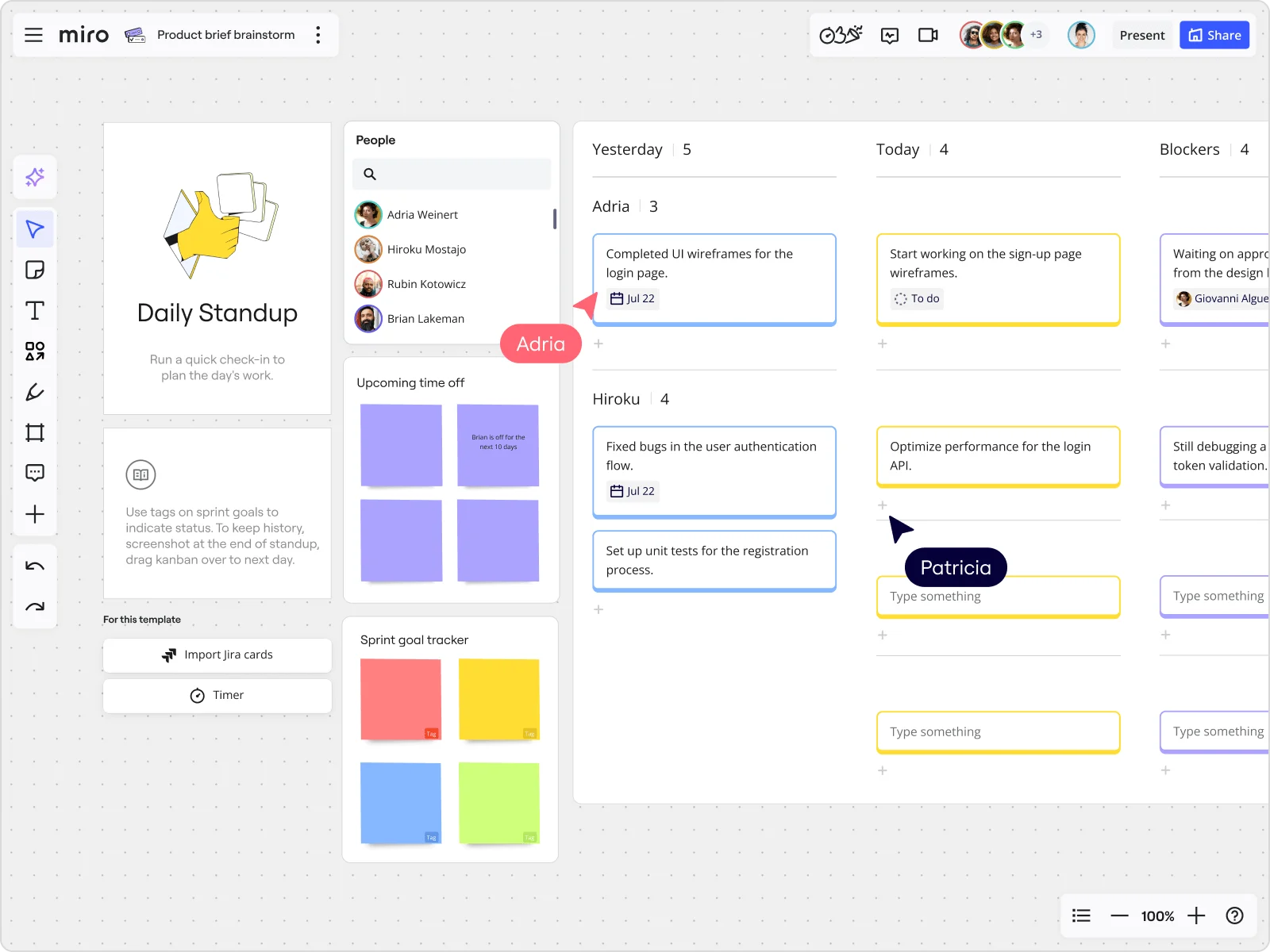
Best practices for managing Scrumban teams
For Scrumban teams to perform at their best, focus on clear communication, adaptability, and efficient workflow management. Here are some essential practices to keep in mind:
1. Encourage regular retrospectives
Hold consistent retrospectives to review successes, identify challenges, and make adjustments. This regular feedback loop helps your team keep improving.
2. Maintain visible WIP limits
Set and review WIP limits to avoid bottlenecks and keep team members from feeling overwhelmed. Reassess these limits periodically as your team’s capacity and needs evolve.
3. Use metrics for better insights
Track metrics like lead time and cycle time to assess workflow efficiency. These insights highlight where improvements are needed and can guide adjustments for smoother processes.
4. Foster open communication
Encourage team members to voice their challenges, ideas, and suggestions. A culture of open dialogue strengthens trust and leads to faster problem-solving.
5. Adapt the board as needed
Let your Kanban board evolve with the team’s changing needs. Add, adjust, or reorganize columns to reflect updates in your workflow, ensuring it stays relevant and helpful.
6. Prioritize continuous improvement
Commit to small, ongoing improvements rather than large overhauls. By consistently refining processes, the team can grow organically and make sustainable progress.
Run Scrumban events in Miro
Ready to try Scrumban on your team? Keep things smooth by having the right tool on hand. Miro makes it easy to host Agile team events, with intuitive tools to build your own Scrum board and plenty of customizable and interactive templates to help you save time. Plus, with powerful features to support both real-time and async collaboration, Miro makes teamwork seamless — for both in-person and distributed teams.
Sign up to get started.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 3, 2025