About the Cost Benefit Analysis Template
Cost benefit analysis (CBA) is an analytical tool that helps your team assess the pros and cons of moving forward with a business proposal. This technique helps you decide the best course of action to take with a new project by analyzing each option.
How to use this template
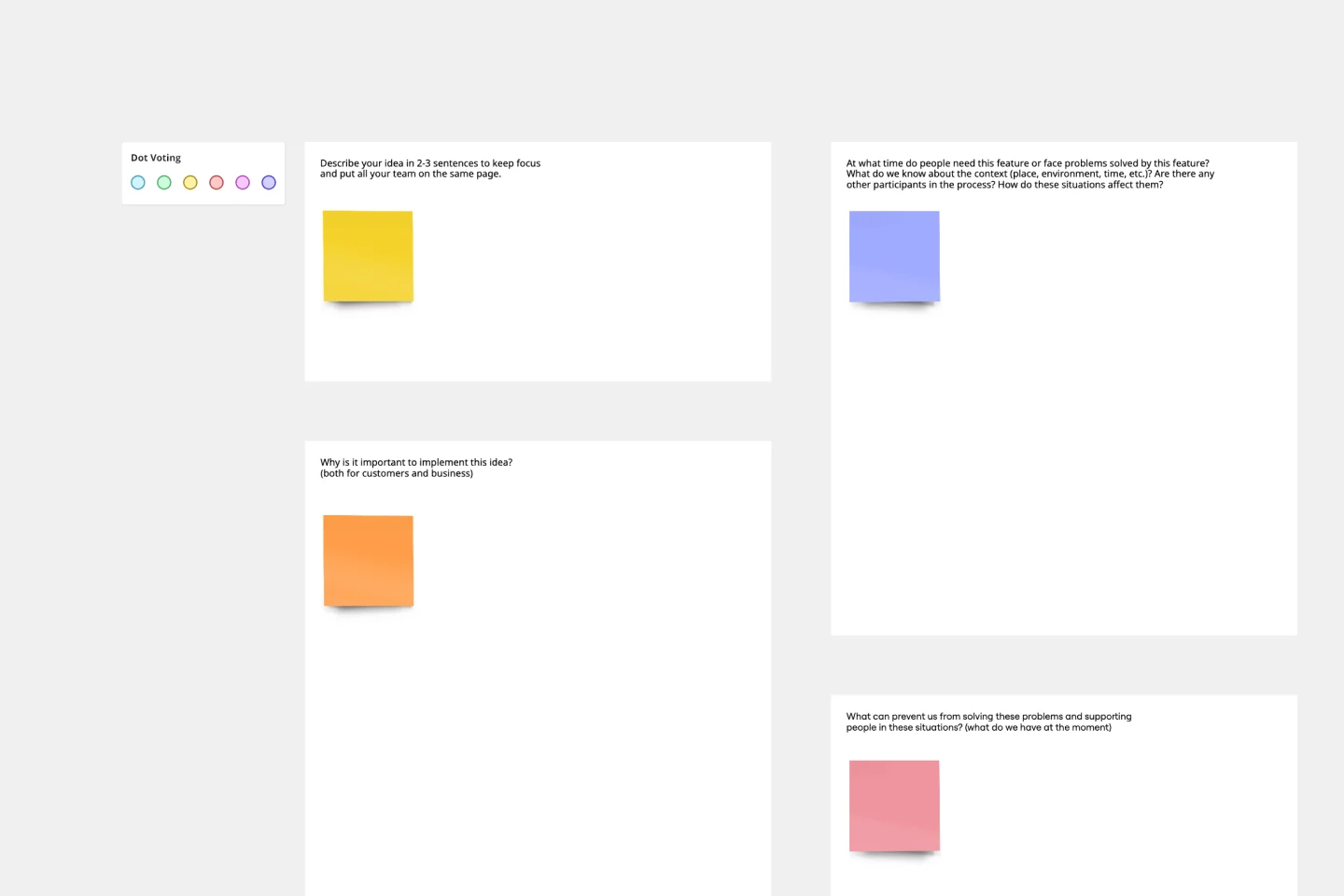
The template you see uses a four-quadrant matrix to help visualize the results of your analysis, often referred to as a Benefit-Cost Analysis Matrix. You can use sticky notes or cards to represent ideas or tasks and place them into the appropriate section based on effort (Cost) and reward (Benefit).
Brainstorm and List: Start by listing all potential costs and benefits, including unexpected or "soft" benefits like employee satisfaction or positive word-of-mouth.
Assign Value: Determine the monetary or numerical value of both the costs and the benefits to quantify the impact of each factor.
Place on the Matrix: Drag and drop your cost/benefit items onto the relevant quadrant:
High Effort/Low Reward (Administrative Tasks): Items that cost a lot of time/money but offer minimal payoff.
High Effort/High Reward (Standard Workflow): Major initiatives with high cost but significant returns.
Low Effort/Low Reward (Gimmicks & Novelties): Small, easy wins with minimal impact.
Low Effort/High Reward (Delightful Features): The most desirable projects, easy to implement, high payoff.
Compare and Decide: Use the visual clusters to determine which option offers the best value and aligns with your strategic goals.
Ready to transform your decision-making? Start your analysis now!