Project charter templates
Miro's project charter templates help you define project goals and align teams effortlessly. Whether you're planning, strategizing, or managing projects, these templates provide a clear structure to outline objectives, assign roles, and set your project up for success.
13 templates
- 105 likes529 uses
- 8 likes450 uses

Project Schedule
The Project Timeline Template simplifies project management. Illustrating tasks, milestones, and deliverables on a calendar visually shows teams a project's progression. One of its standout benefits is its ability to foster clarity. With this template, project milestones are translated into an easily digestible format, enabling team members to quickly comprehend the entirety of the project's scope and sequence, thereby enhancing productivity and reducing potential misunderstandings.
- 9 likes355 uses
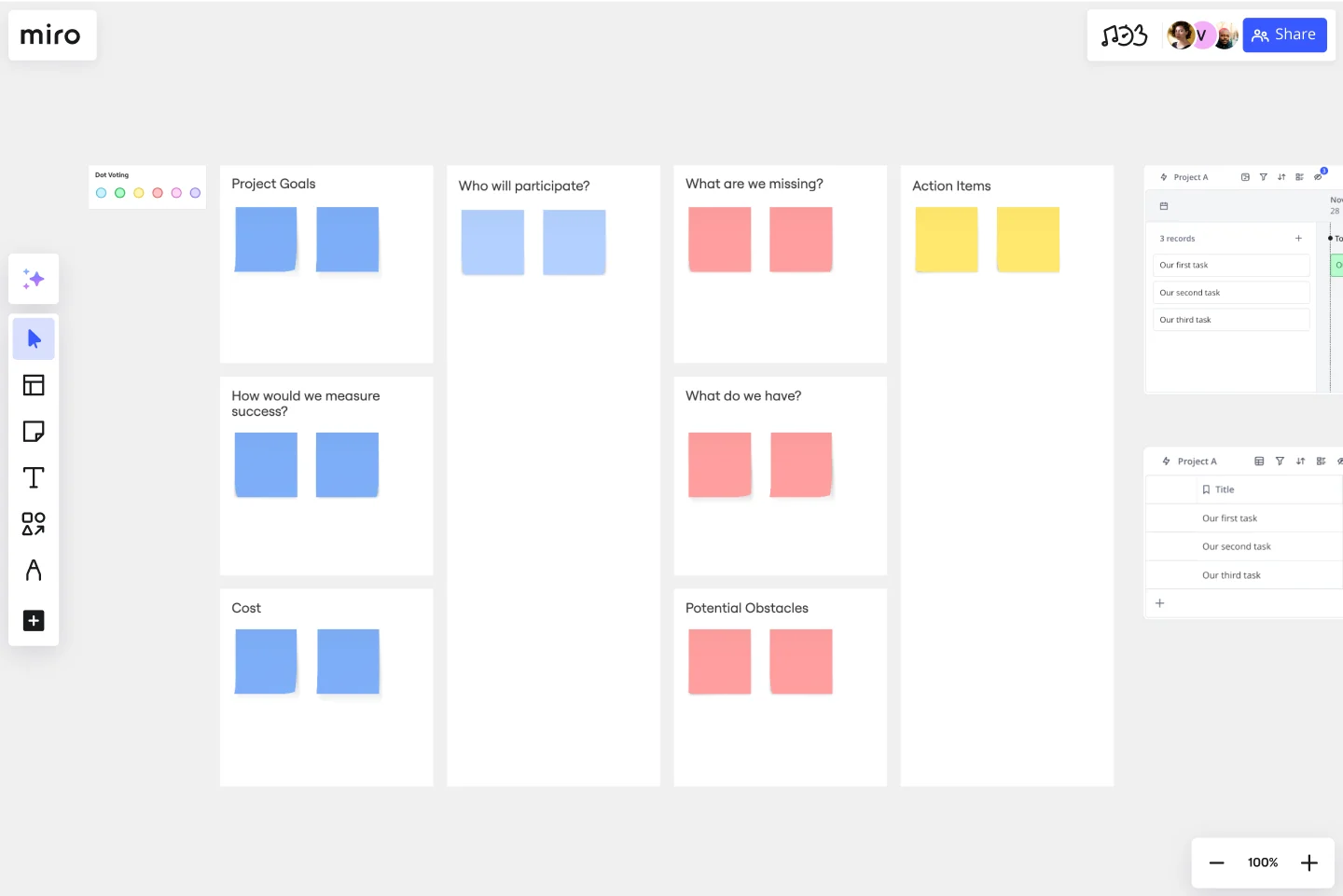
Project Planning Template
A project plan is a single source of truth that helps teams visualize and reach project milestones. Project plans are most useful when you outline the project’s “what” and “why” to anyone who needs to give you project buy-in. Use a project plan to proactively discuss team needs; expectations; and baselines for timeline, budget, and scope. The plan will also help you clarify available resources before you kick off a project, as well as expected deliverables at the end of the project.
- 7 likes305 uses

Project Canvas Template
A project canvas is a management tool that helps you summarize, visualize, and share all necessary information about your project. It can be used by all team members—from facilitators to project management professionals—at every stage of project development. The project canvas template allows you to keep all stakeholders in the project development process in the loop. By using a single platform for all project-related discussions, you can build a clear project overview and improve collaboration.
- 2 likes230 uses
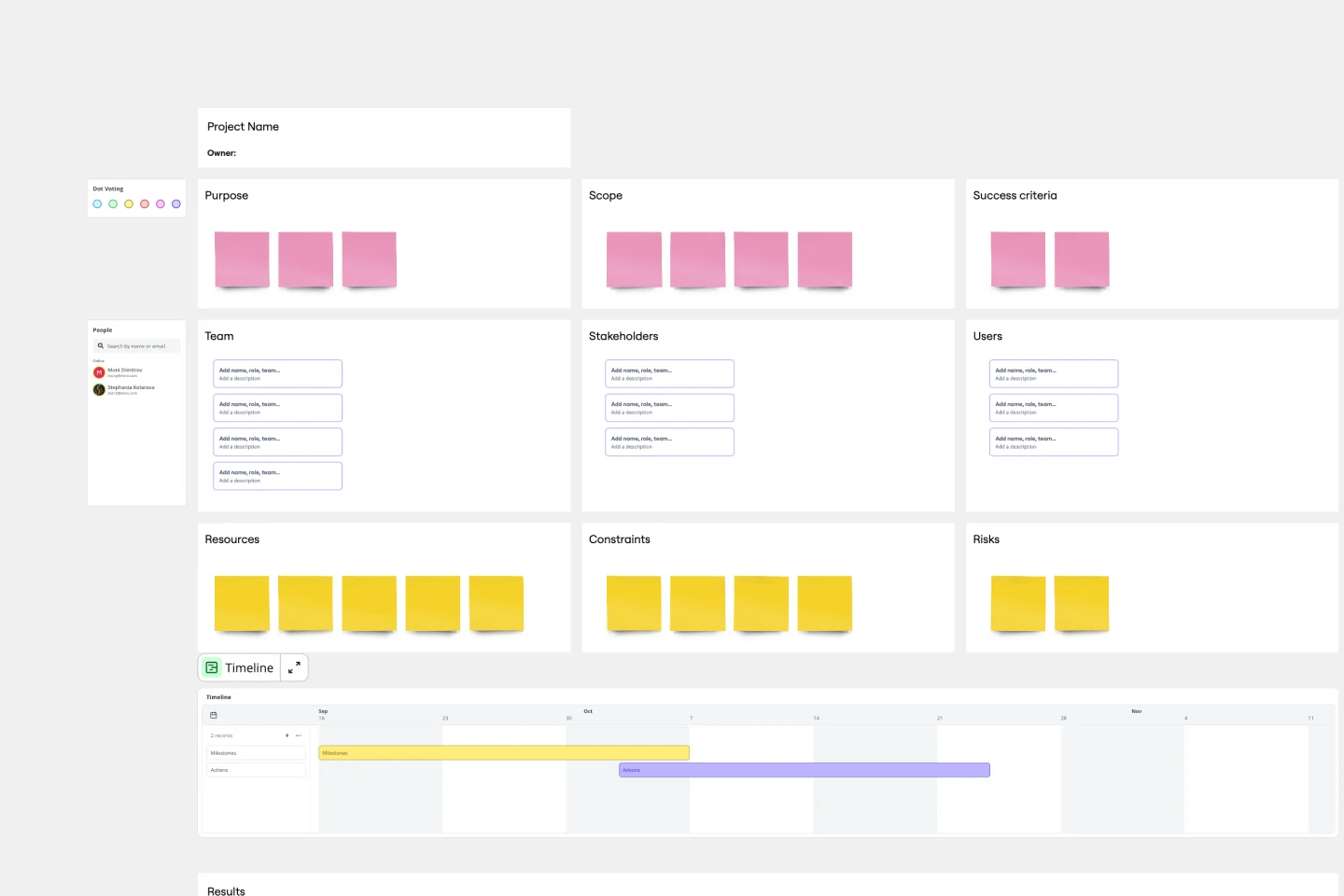
Project Charter Template
Project managers rely on project charters as a source of truth for the details of a project. Project charters explain the core objectives, scope, team members and more involved in a project. For an organized project management, charters can be useful to align everyone around a shared understanding of the objectives, strategies and deliverables for a project of any scope. This template ensures that you document all aspects of a project so all stakeholders are informed and on the same page. Always know where your project is going, its purpose, and its scope.
- 70 likes223 uses
- 12 likes191 uses
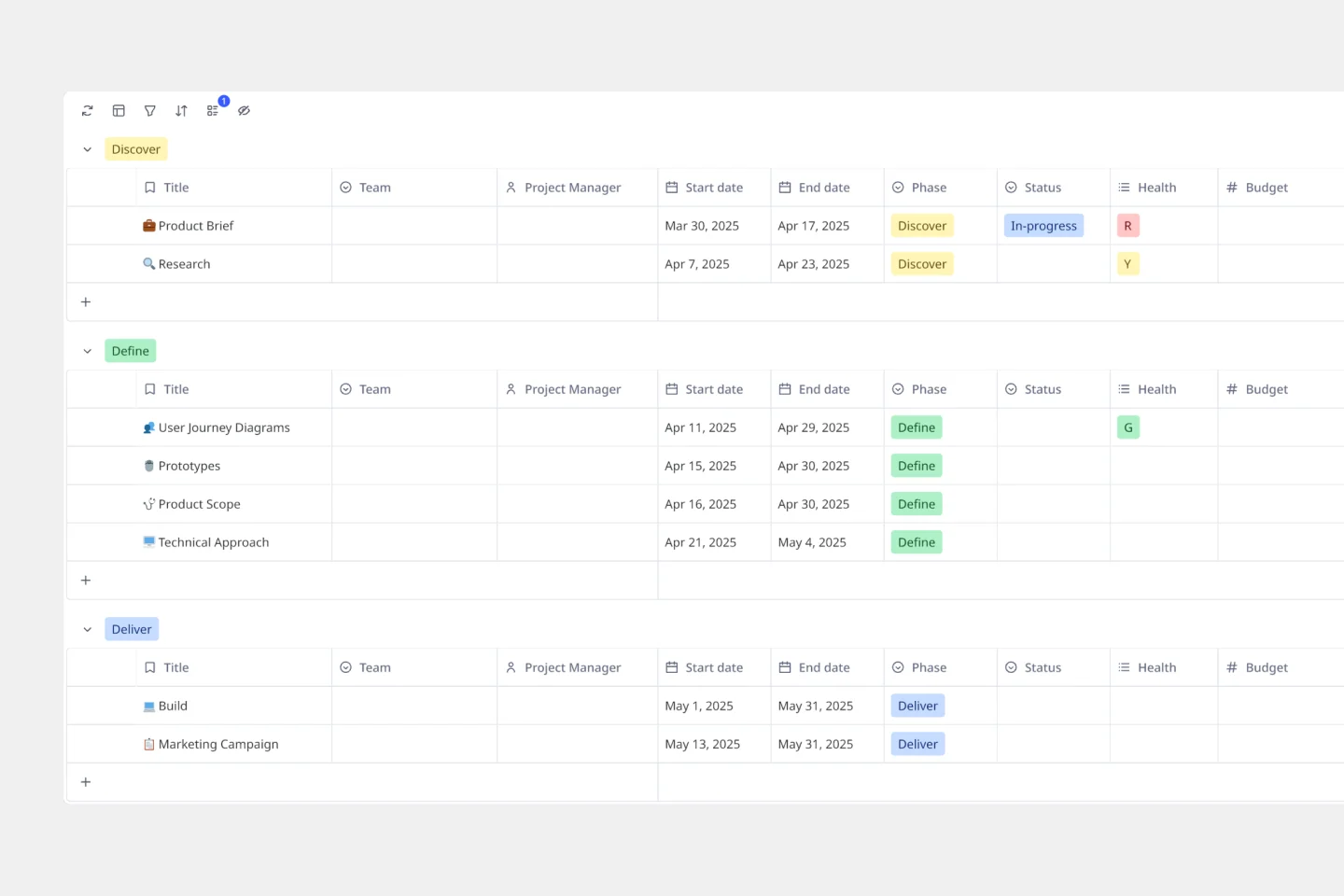
Project Tracker
Scattered project updates across emails, Slack threads, and random spreadsheets making it impossible to see the big picture? A project tracker template brings all your project details into one visual workspace. Track milestones, monitor team progress, assign ownership, and spot potential roadblocks before they derail your timeline. Use Miro's AI-powered project tracker template to instantly organize complex projects and keep everyone moving toward the same goals.
- 6 likes144 uses
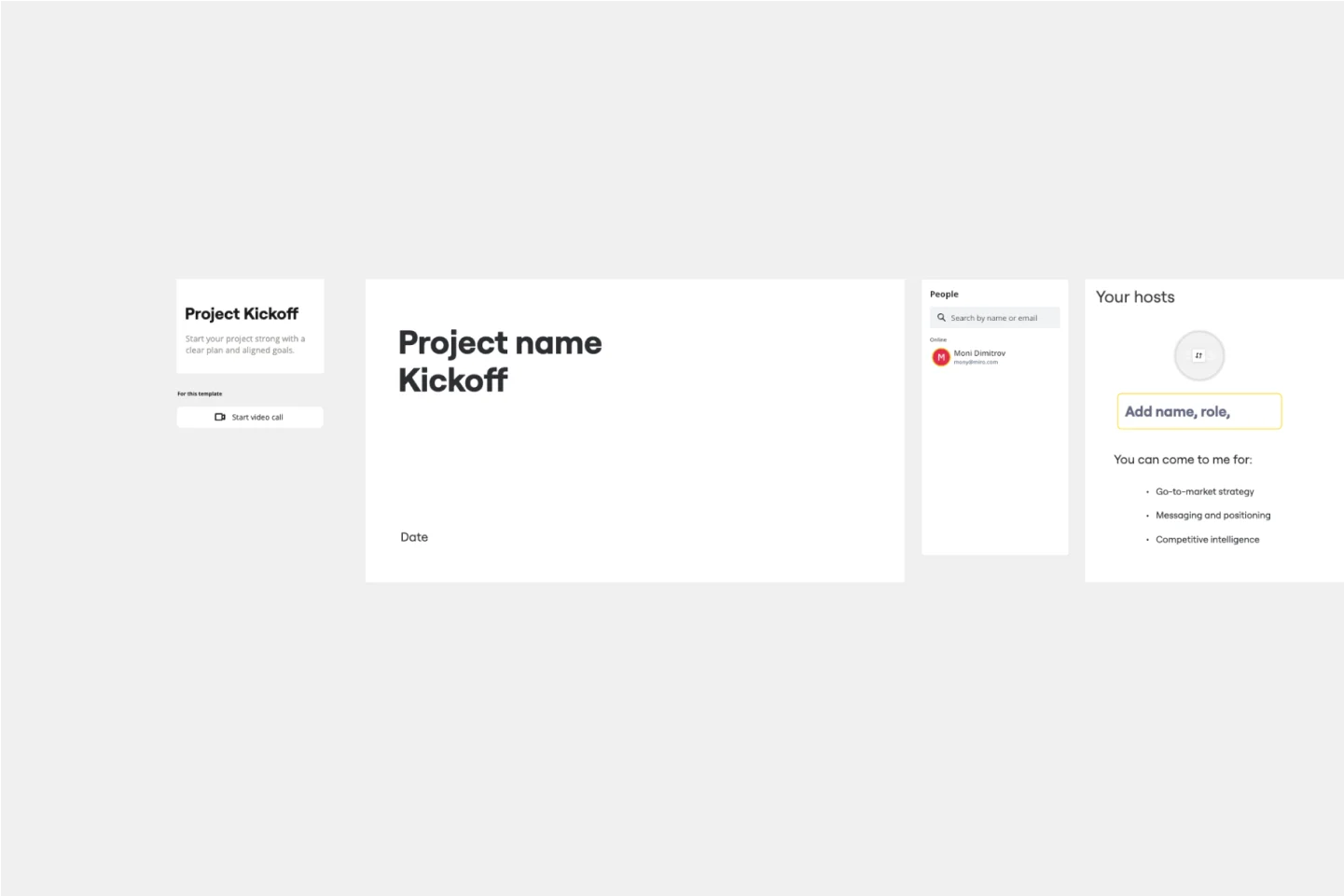
Project Kickoff Template
This Project Kickoff Meeting Template helps you have all the information about your project in one shared space, like a project manifesto. This template has seven activities to define your project’s goals and objectives, the team’s roles and responsibilities, and the next steps and resource materials for further consultation. Use the Project Kickoff Meeting Template to manage projects effectively and keep everyone aligned.
- 0 likes137 uses
Project Status Report Template
When a project is in motion, the project manager must keep clients and shareholders updated on the project’s progress. Rather than waste time with constant meetings, leaders can send out weekly or daily project status reports to keep everyone informed. You can use the Project Status Report Template to streamline the report creation and distribution process.
- 3 likes88 uses

Project Scope Template
A project scope helps you plan and confirm your project’s goals, deliverables, features, functions, tasks, costs, and deadlines. A project manager and team should develop a project scope as early as possible, as it will directly influence both the schedule and cost of a project as it progresses. Though project scopes will vary depending on your team and objectives, they generally include goals, requirements, major deliverables, assumptions, and constraints. Aim to include the whole team when you create a project scope to ensure everyone is aligned on responsibilities and deadlines.
- 2 likes68 uses
Project Proposal Template
For any type of project, the Project Proposal template can be a crucial step toward clarifying the context, goals, and scope of a project to get stakeholder buy-in. A project proposal outlines what you want to accomplish, your goals, and how you plan to achieve them. Generally, a project proposal gives the reader some context on the project, explains why it is important, and lists the actions that you will take to complete it. Project proposals have myriad uses. Often, businesses use project proposals to get external buy-in from a donor or outside stakeholder. But many companies draw up project proposals for internal buy-in too.
- 1 likes22 uses
AI Accelerated
Project Review AI Template
The Intelligent Project Review Template in Miro is a game-changer for project management. It combines AI-driven insights with interactive features to streamline the review process, making it more efficient and collaborative. One key benefit of this template is its ability to enhance team alignment. By providing a structured format for documenting timelines, hypotheses, target audiences, success metrics, and potential blockers, it ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page, fostering a shared understanding and confidence in the project's direction.
- 0 likes9 uses

Project Review Template
The Intelligent Project Review Template in Miro is a game-changer for project management. It combines AI-driven insights with interactive features to streamline the review process, making it more efficient and collaborative. One key benefit of this template is its ability to enhance team alignment. By providing a structured format for documenting timelines, hypotheses, target audiences, success metrics, and potential blockers, it ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page, fostering a shared understanding and confidence in the project's direction.
Explore more
About the Project Charter Templates Collection
Project charters are essential documents that formally authorize the existence of a project and provide the project manager with the authority to apply organizational resources to project activities. Miro's project charter templates are designed to streamline this process, offering a variety of customizable options to suit different project needs. These templates are perfect for project managers looking to kickstart their projects with clarity and precision. With Miro's intuitive interface, you can easily adapt each template to fit your specific requirements, ensuring that all critical aspects of your project are covered from the get-go.
Why you'll love our project charter templates
Using Miro's project charter templates comes with a host of benefits that can significantly enhance your project planning and execution:
Visual planning: Miro's visual planning tools make it easy to map out your project from start to finish. The drag-and-drop interface allows you to create a clear and comprehensive project charter that everyone on your team can understand.
Timeline widget: Keep your project on track with Miro's timeline widget. This feature helps you visualize your project schedule, set milestones, and track progress in real time.
Miro cards: Use Miro cards to break down your project into manageable tasks. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and monitor progress all in one place.
Task management: Miro's task management capabilities ensure that nothing falls through the cracks. You can assign tasks, set priorities, and track completion, making it easier to manage your team's workload and stay on top of project deliverables.
Collaboration: Miro's collaborative features allow your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of location. Share your project charter with stakeholders, gather feedback, and make real-time updates to keep everyone aligned.
How to use the project charter templates in Miro
Using Miro's project charter templates is straightforward and user-friendly. Follow these steps to get started:
Select a template: Browse through Miro's collection of project charter templates and choose the one that best fits your project needs. You can find templates for various types of projects, from simple to complex.
Customize the template: Once you've selected a template, customize it to suit your project. Add your project name, objectives, key metrics, deliverables, budget, and stakeholders. Miro's intuitive interface makes it easy to edit and personalize each section.
Add visual elements: Enhance your project charter with visual elements like timelines, Miro cards, and task lists. These tools help you create a clear and engaging document that is easy to understand and follow.
Collaborate with your team: Share your project charter with your team and stakeholders. Use Miro's collaborative features to gather feedback, make real-time updates, and ensure everyone is on the same page.
Monitor and update: As your project progresses, use Miro to monitor progress and make necessary updates to your project charter. This ensures that your document remains a living, dynamic tool that evolves with your project.
By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive and effective project charter that sets your team up for success. Miro's project charter templates are designed to help you plan, execute, and manage your projects with ease, ensuring that your team can thrive and achieve their goals.

