Table of contents
Table of contents
What is an empathy map?

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
- What an empathy map is and how it helps product and UX teams understand users from multiple perspectives
- The key components or quadrants of an empathy map, such as what users say, think, do, and feel
- How to identify your target user and gather relevant research data before creating the map
- Step-by-step instructions on filling out an empathy map using customizable templates
- The importance of team collaboration in refining the empathy map and incorporating feedback
- How to apply insights from the empathy map to improve user experience and align product design with user needs
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Empathy mapping: Everything you need to know
An empathy map helps product teams and UX teams develop a deeper understanding of their users. The empathy map encourages UX and product designers to create UX designs and usability features from a user-centered perspective. As a result, they can better serve the needs and wants of users.
Empathy mapping is also part of the design-thinking process, an iterative and customer-centered way of solving problems and creating new products or services. It allows Agile teams to prioritize customer needs in their sprints and iterations.

What are the 4 aspects of a customer empathy map?
Empathy maps usually have four quadrants: says, thinks, sees, and hears.
However, the exact content of the quadrants varies from business to business. Some empathy maps also cover what a customer does and feels. Other maps also identify the target audience, address key pain points and challenges, and describe what customers hope to gain from using the product or service.
Let’s look at these areas in more detail:
Says
This quadrant outlines what the user says. What do they want from your product or service? It’s usually direct quotes from users taken verbatim from usability studies, consumer reviews, and user interviews. For example, “I want something intuitive.”
Thinks
Use this quadrant to capture what the user is thinking throughout the buying and user experience. Based on your own or third-party research, you can see what your users value about the experience and how you can meet their needs.
Sees
With the ‘sees’ quadrant, you’ll cover any physical elements that the user sees throughout the experience. Your website, customer reviews, emails, paid ads, and social media posts are all examples of what users might see while engaging with your business.
Hears
This quadrant tends to focus on word of mouth and any recommendations or words-of-warning received from friends or family. An example might be a close friend recommending your company because of its excellent customer service.
Does
Here, you’ll clarify the physical actions that your users take throughout their experience. An example might be searching for your product or service online or navigating your website.
Feels
This section represents the emotional state of your user. It should outline their concerns, likes, dislikes, and anything else that indicates how they feel about the experience. For example, impatience when a page loads too slowly.
Pain points
In this section, you’ll cover any challenges and hurdles that your customers face while moving through the user experience. This will help you pinpoint areas of improvement.
Gains
To fully understand how to provide value to your customers, you need to know what they want from you. In this quadrant, you’ll outline exactly what your users hope to gain from the experience and the end product or service.
People are complex, so it’s not unusual to have some conflicting information within an empathy map. You might also come across some inconsistencies, and that’s perfectly normal. Although this information can be confusing, it’s still useful. It helps you uncover the root of their emotions, investigate the cause of any conflict, and find the best way to resolve it.
Who is the user in an empathy map?
The user is the audience group you’re trying to target. Creating the empathy map allows you to understand and empathize with them, which gives you a deeper understanding of what they want from your business.
If you have multiple user groups, each one will need their own empathy map. For example, you might target female users aged 35–44. However, you might also target male users in the same age group.
These two different demographics will likely have different perceptions, needs, and wants. Creating a separate empathy map for each audience group allows you to better serve their needs and create a personalized experience.
What is the difference between user persona and empathy map?
Although user personas and empathy maps are similar, they’re not the same.
A user persona helps you visualize your target customer. It focuses on the attributes that define your users, including demographics, personality traits, skills, and so on.
In contrast, empathy maps focus more on what your customers want and how they feel as opposed to who they are. They tell you what your customers' attitudes and behaviors are, and how they feel about the buying and user experience.
Another key difference is that personas are based on fictional users that represent a target audience group. Empathy maps are informed by research gathered from real people.
When to use an empathy map
Let’s take a look at some situations where you might consider using an empathy map.
To improve the user experience (UX)
If you’re looking for a way to improve your user design, but you’re not sure where to start, an empathy map is a good idea. It helps you visualize what your customers want and how they move through the user experience. This can highlight key areas of development when it comes to the UX of your website.
To launch a new product
With a new product idea, you need to make sure that potential users are on board with any new product ideas. Using an empathy map helps you visualize what your customers want and how a new product can provide value and meet their needs.
To refine the customer experience
There are a lot of elements that form the customer experience. Because of this, it can be hard to identify areas of improvement. With an empathy map, you can clarify exactly what your customers are thinking and feeling. It helps you find the root of any problem, allowing you to fix it and provide them with a better overall experience.
Why is it important to empathize with your user?
Creating an empathy user map has a lot of benefits for businesses. Gaining customer insights, offering a better customer experience, and developing a better understanding of their customers are just a few of the key benefits.
Let's take a look at these in more detail.
Gain valuable customer insights
An empathy map forces you to analyze the user experience from the user’s perspective. As a result, you have access to valuable customer insights. For example, you’ll better understand what your customers are thinking, feeling, and saying about your company and your product or service. With this information, you can make informed decisions about business growth and development.
Offer a better customer experience
When you know more about your customers, you can provide them with a better experience. You can personalize communications, streamline the buying process, and offer them an experience that’s tailored to their needs. A better customer experience improves retention and increases repeat business. Happy customers also become advocates for your products and services.
Provide a product or service with more value
Creating an empathy map allows you to analyze exactly what users want from your product or service. This means you can create something that has as much value as possible for the user. Your customers get a better product or service, and you get a happier customer — it’s a win-win.
Example of an empathy map
In the below example of an empathy map, you can see how a user who is a travel enthusiast outlines their motivations, needs, and pain points.
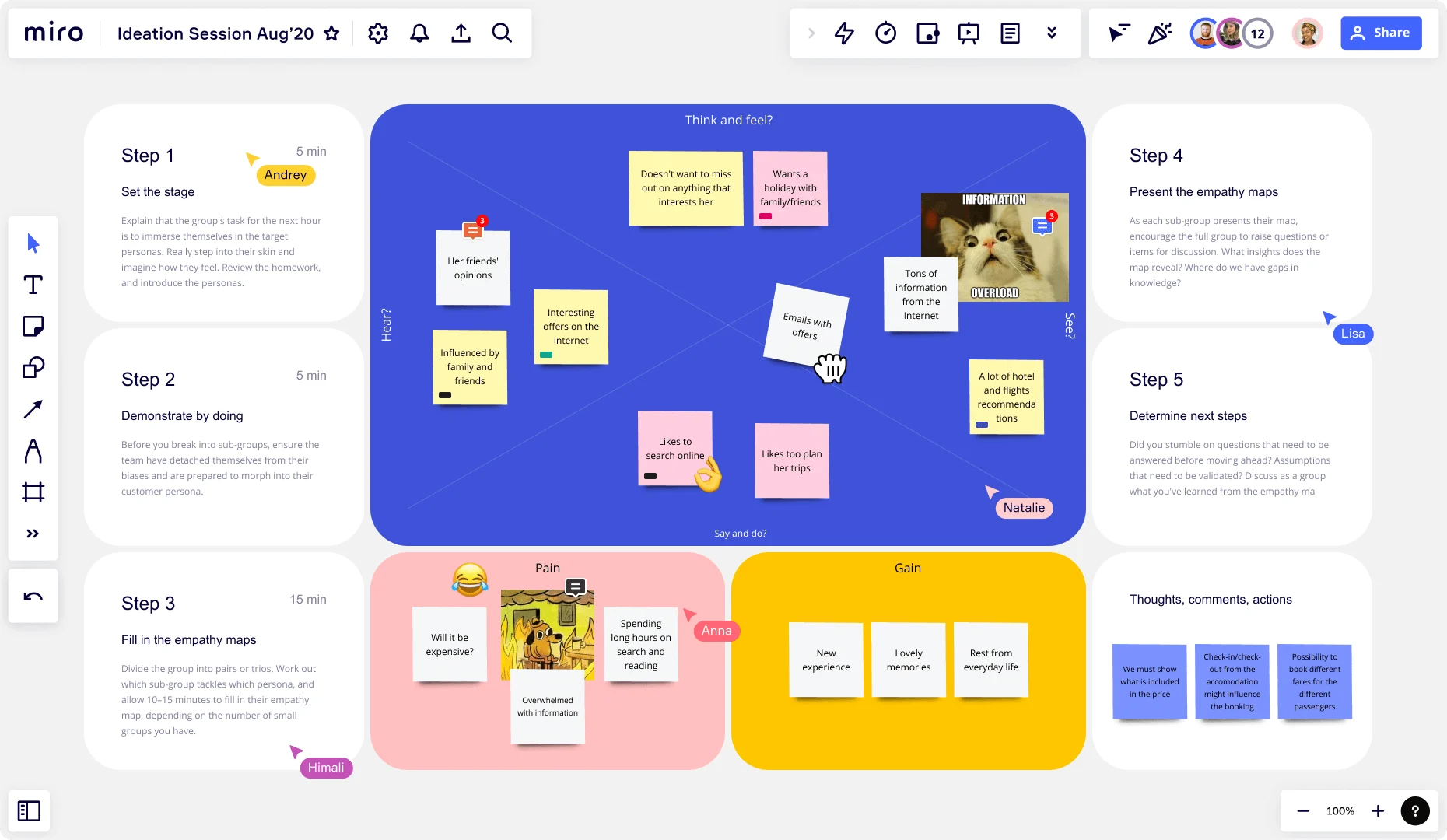
The map captures insights about the user’s feelings, such as not wanting to miss out on exciting adventures and wanting to plan trips with family and friends. The user is motivated by hearing about the opinions and experiences of trusted family members and friends. Though this user likes to plan, they are adverse to feeling overwhelmed by too much information and having to spend long hours doing research.
How to create and use an empathy map
Let’s walk through the five simple steps you can follow to create an empathy map of your own.
Identify your target user
Start by identifying who it is you want to empathize with. Without this information, your empathy map will lack clarity and direction — both of which you need to better understand your customer.
If you’re not sure who your target user is, take a look at Miro’s Target Audience Template to start on the right foot.
Using the template, you’ll outline all the key information about your audience to help you identify exactly who they are. With this information, you’ll be able to create a clear and concise empathy map that accurately reflects your target user.
Once you’ve identified your target user, gather together any customer research data or information you have on this particular user group.
Define your desired outcome
Defining your purpose and outcome is an important part of the mapping process. It gives you direction and makes sure that you’re collecting information that’s relevant to your goals as a business.
Do you want to improve the customer experience? Add more customer value? Streamline the user experience? Whatever it is, be clear about this before you start mapping.
Fill in the empathy map
With a clear picture of your ideal customers and your desired outcome, you can now start plotting your empathy map.
This is where using Miro’s free Empathy Map Templates comes in handy. Using one of our templates, you can instantly start adding your notes about who your audience is and what they think, see, hear, and do.
Our empathy map canvas is also customizable, so you can remove sections from our existing template and replace them with quadrants that are better suited to what you’re looking for. You can add new text, upload images, and even change the font to keep the template on brand.
There’s no right or wrong way to fill in your map. Add the information however you see fit. Over time, you’ll create a visual of who your audience is, what they want, and how you can serve their needs.
Share the map with your team
Share the finished empathy map with the relevant stakeholders to get feedback. This is their chance to ask questions, offer suggestions, and make any notes on the information you’ve collected.
If you use Miro to create your map, you can easily share it with both internal and external stakeholders to gather feedback, then review their suggestions and make any necessary changes.
Apply what you’ve learned
The map is finished, and now it’s time to put what you’ve learned into practice. The best way to do this is to create an action plan. This will identify the areas where you provide the most customer value in the shortest amount of time. Hopefully, this will also get you the quickest results.
As time goes on, you may need to revisit the empathy map to keep it up to date. Customer needs change, and what they want from you and your business will also change. It’s important that you continually return to this information to make sure your business continues to provide users with the best experience, product, or service possible.
Create your next empathy map with Miro
Empathy mapping is a valuable tool for businesses looking to deepen their understanding of who their customers are and what they want. It forces teams to empathize with users, provides insights for product development, and helps businesses improve the user experience.
Get started by using Miro’s free Empathy Map Template to gain a better understanding of your customers and what matters most to them.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 22, 2025