Customer Experience vs. Service Design

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
- The fundamental difference between Customer Experience (CX) and Service Design (SD): CX optimizes individual touchpoints and emotions, while SD targets internal processes and systems for seamless service delivery.
- CX aims to enhance satisfaction, loyalty, and emotional engagement, whereas SD focuses on improving operational efficiency and reducing customer effort.
- How CX and SD overlap and complement each other, with CX principles informing SD strategies and SD ensuring consistent experiences.
- The role of service design in bridging organizational silos by aligning people, processes, and tools for sustainable customer experience.
- Examples illustrating CX as end-user interaction (e.g., mobile app) and SD as broader backend design (e.g., airport check-in).
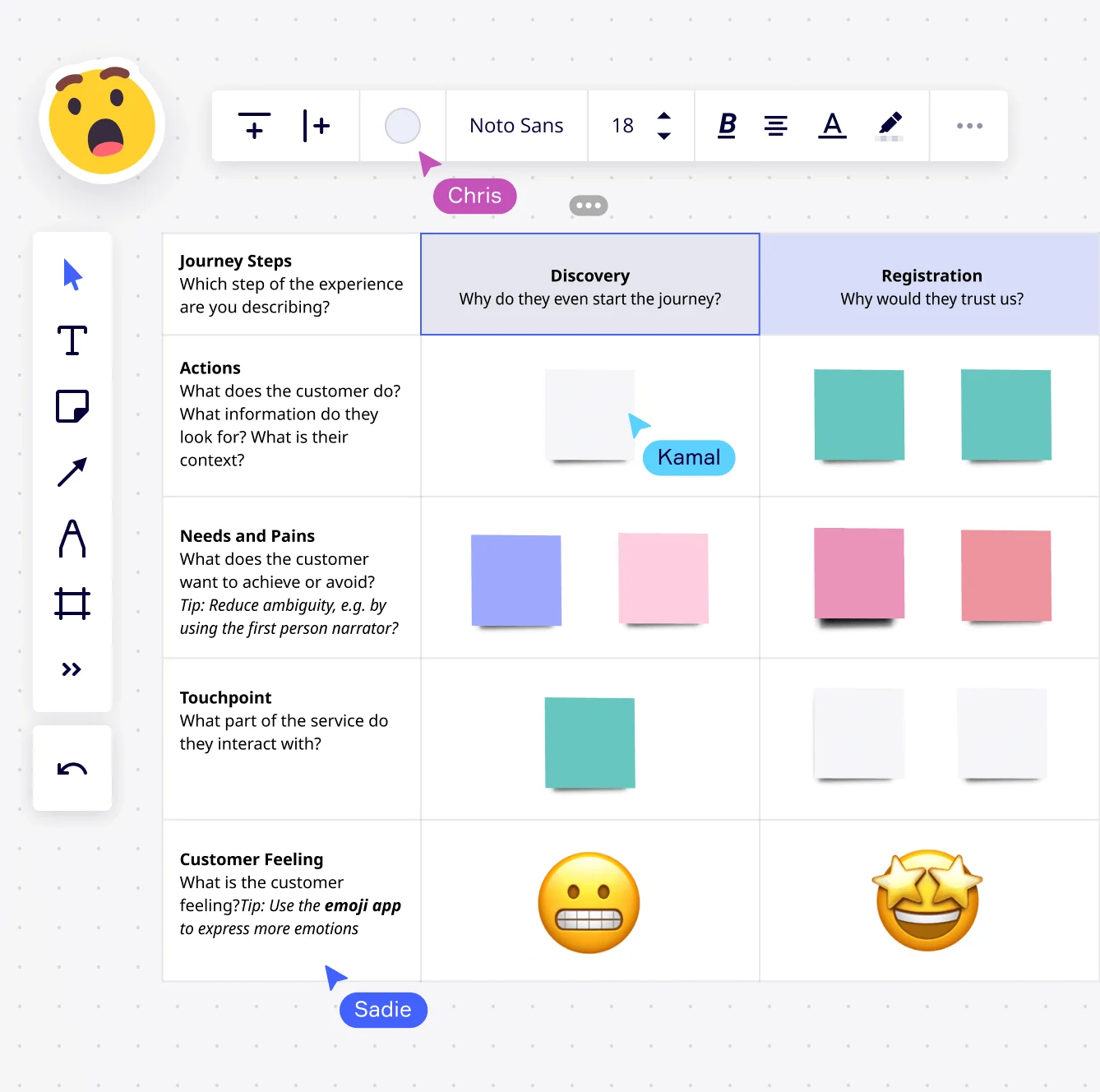
- The importance of using tools like service blueprints and customer journey maps to visualize and optimize customer-facing and internal workflows for better experience outcomes.
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Customer Experience and Service Design
Discover the transformative power that lies at the crossroads of customer experience (CX) and service design (SD). In a world where customer loyalty and satisfaction reign supreme, understanding the nuances between CX and SD is the key to unlocking unparalleled business excellence.
In this guide, we'll cover the untapped potential of CX and SD, and how to propel your organization to new heights of success in the modern market.
Understanding Customer Experience
Customer experience goes beyond mere transactions; it encompasses the entire journey a customer takes with a brand.
Here's what you need to know about CX:
• Definition of Customer Experience: Customer experience refers to the sum of all interactions and touchpoints a customer has with a brand, product, or service throughout their entire lifecycle.
• Importance of Customer Experience in Business: CX directly impacts customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy, making it a powerful driver of brand success.
• Elements of a Positive Customer Experience: Key components include personalized interactions, seamless omnichannel experiences, and proactive issue resolution.
Understanding Service Design
Service design revolves around creating and optimizing processes, systems, and touchpoints to deliver exceptional services.
Let's take a closer look at service design:
• Definition of Service Design: Service design is the strategic and holistic approach to designing, aligning, and continuously improving services to meet customer needs and enhance operational efficiency.
• Importance of Service Design in Business: Service design drives customer-centricity, process efficiency, and innovation, ultimately elevating the overall service quality.
• Elements of Effective Service Design: Considerations include user-centric design, service blueprints, and service prototyping.
Key Differences Between CX and SD
While CX and SD share the ultimate goal of customer satisfaction, they diverge in focus, objectives, and implementation:
Focus and Scope:
• Customer-Centric Approach in CX: CX revolves around understanding and meeting customer expectations and emotions at each touchpoint.
• System-Centric Approach in Service Design: SD centers on designing and optimizing internal processes and systems to ensure seamless service delivery.
Goal and Objectives:
• Customer Experience: Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: CX efforts aim to foster positive emotions, brand loyalty, and repeat business from satisfied customers.
• Service Design: Improving Efficiency and User Experience: SD targets process efficiency, reducing customer effort, and enhancing the overall user experience.
Implementation and Execution:
• Customer Experience: Across Various Touchpoints and Interactions: CX initiatives span all customer interactions, including marketing, sales, support, and post-purchase experiences.
• Service Design: In Specific Service Processes and Systems: SD interventions occur within service processes, optimizing internal operations while aligning with customer needs.
Measurement and Evaluation:
• Customer Experience: Metrics like NPS, CSAT, and Customer Churn: CX success is often gauged through metrics that assess customer sentiment and loyalty.
• Service Design: Metrics like Service Efficiency and Error Rates: SD success is measured by process efficiency, error rates, and service delivery speed.
Overlapping Aspects and Synergies
While CX and SD differ in their primary focus, there are areas where they intersect, creating powerful synergies:
Customer-Centricity in Service Design:
• CX principles play a pivotal role in shaping service design strategies.
• A deep understanding of customer needs informs the creation of user-centered services.
Seamless Experience through Service Design:
• SD ensures that CX is consistent and seamless across all touchpoints.
• Aligning processes with customer expectations enhances the overall experience.
Integrating Customer Experience and Service Design
To leverage the full potential of CX and SD, businesses should aim for integration and collaboration:
Creating a Unified Approach:
• Align CX and SD strategies to create a cohesive customer journey.
• Foster collaboration between CX and SD teams to develop customer-centric processes.
Collaborative Team Efforts:
• Break silos and encourage cross-functional collaboration.
• Promote shared goals and KPIs to foster a customer-first culture.
Future Trends and Innovations
As the business landscape evolves, CX and SD continue to evolve with emerging trends:
The Evolving Landscape of Customer Experience:
- Embrace emerging technologies like AI, VR, and AR to elevate CX.
- Leverage data analytics for hyper-personalized experiences.
Advancements in Service Design:
- Integrate AI and automation for improved service efficiency.
- Implement design thinking methodologies for continuous innovation.
Miro’s UX design tool is powerful and will help you and your team innovate as the world evolves. Enhance your design collaboration using Miro’s infinite workspace for in-person, hybrid, or remote work.
Conclusion: Customer Experience vs Service Design
In the dynamic realm of customer experience and service design, businesses must grasp the nuanced differences between the two and harness their synergies to thrive. By embracing a customer-centric mindset and optimizing internal processes, organizations can craft remarkable experiences that propel them to the forefront of their industries.
Remember, the key lies in aligning the principles of customer experience and service design to achieve excellence and sustain success. Adaptability and continuous improvement are the keys to staying ahead in an ever-evolving market. Embrace the power of CX and SD, and your business will be well-positioned to triumph in the digital age.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 22, 2025