Mental models and the decision-making process

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
- What mental models are
- Connection to decision-making
- Types of mental models
- Improve decisions with mental models
- Pitfalls of mental models
- Create and use mental models collaboratively
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
What effect do mental models have on the decision-making process?
Mental models are frameworks that give people a representation of how the world works. These models are ingrained in our cognitive processes and can significantly influence how we approach problems, make decisions, and interpret information. As such, mental models play a significant role in the brainstorming process, helping to frame and understand the problem at hand and come up with structured approach to finding a solution.
Importance of mental models
Mental models are a critical component of brainstorming as they act as templates or guidelines that help process information and reasoning. By using and understanding mental models, individuals can quickly assess a situation, categorize information, and make predictions about likely outcomes. These models form the building blocks of thought, enabling us to connect new information with existing knowledge.
Connection between mental models and decision-making
Mental models shape how we perceive the world and, consequently, how we make decisions. By providing a structured way of thinking about problems, mental models can help in making more informed, coherent, and rational decisions. However, they can also lead to biases or errors if not applied correctly or if the wrong model is used for a particular situation.
Types of mental models
The human mind employs various mental models to make sense of the world. These models can be broadly categorized into different types, each serving unique purposes in thinking and decision-making.
System 1 and System 2 thinking
System 1 and System 2 thinking, proposed by psychologist Daniel Kahneman, describe two modes of thought. System 1 is fast, intuitive, and often subconscious, while System 2 is slower, more analytical, and deliberate. Understanding these two systems helps to identify when we may be relying too heavily on intuition (System 1) or over-analyzing a situation (System 2), allowing for more balanced decision-making.
Heuristics and biases
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that allow people to make quick decisions without having to analyze all available information. While they can be useful, heuristics can also lead to biases, such as overconfidence or stereotyping. Recognizing and understanding these biases can enable individuals to avoid common pitfalls and make more accurate and unbiased decisions.
Other cognitive frameworks
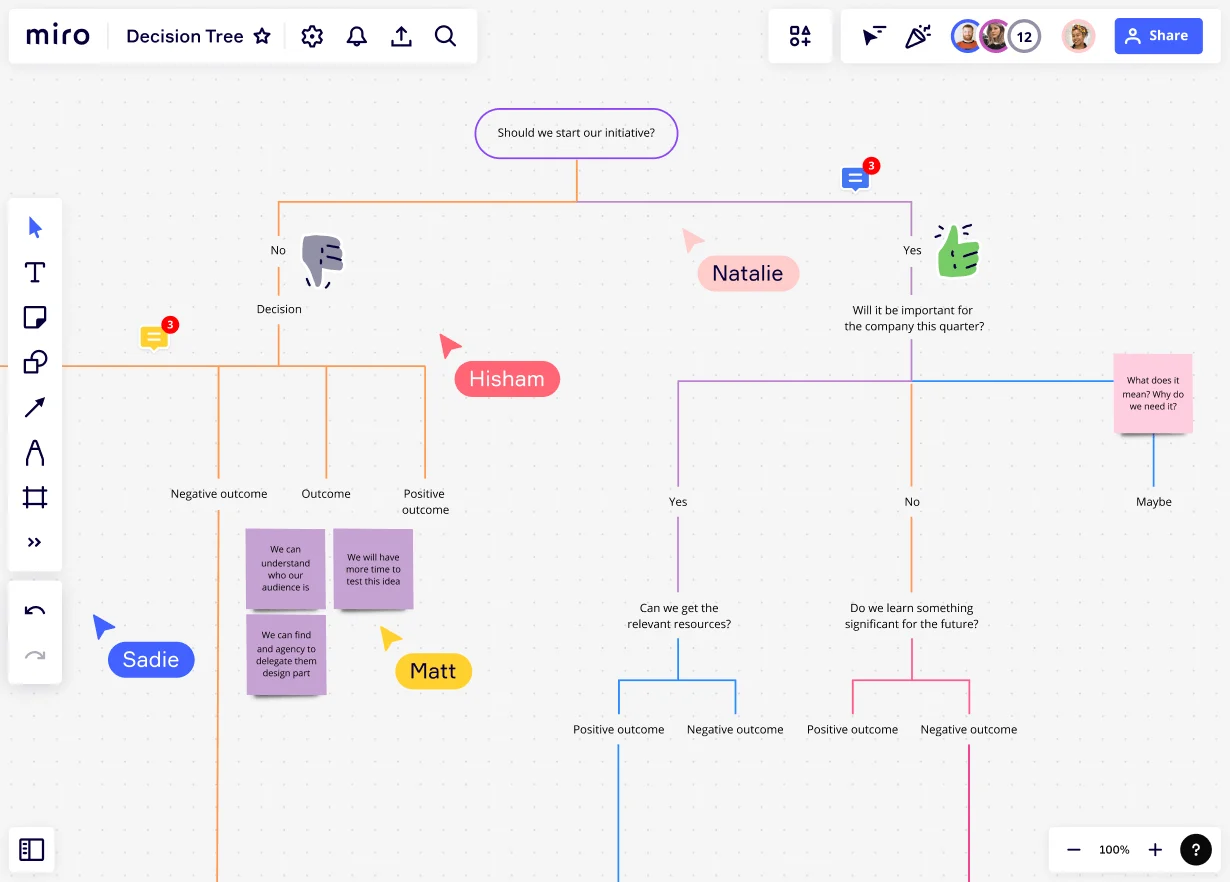
Beyond System 1 and System 2 thinking and heuristics, there are other cognitive frameworks that can assist in decision-making. Examples include decision trees, game theory, and scenario planning. These models provide different approaches to evaluating options, predicting outcomes, and considering multiple variables, allowing for a more comprehensive and nuanced analysis of complex situations.
How mental models influence decision-making
Mental models play a vital role in influencing how we make decisions. They can both enhance and hinder the decision-making process, depending on how they are applied.
Enhancing decision quality
Mental models can greatly enhance decision quality by providing a structured approach to thinking and evaluating options. By employing the right models, individuals can gain clarity, think critically, and make more informed choices. Whether it's using a decision tree to weigh various factors or employing game theory to anticipate others' reactions, mental models can lead to more effective and sound decisions.
Pitfalls and misapplications
While mental models can be highly beneficial, they can also lead to pitfalls and misapplications if not used properly. Relying too heavily on a specific model without considering its limitations, or using a model that doesn't fit the context, can result in poor decisions. Furthermore, biases and errors can stem from over-reliance on heuristics or intuitive thinking. Understanding these potential shortcomings and being mindful of how and when to apply different models is essential for optimal decision-making.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 2, 2025