How do you ensure your product is meeting – and even exceeding – the needs of your customers? It’s a question that companies grapple with every day.
In the summer of 2017, I joined the product team at Cherry Home, a startup developing an AI home security system. At the time Cherry had developed advanced computer vision and AI technology and had started crafting the product story. We had to figure out what our product was going to be and who it was going to serve. To do that, we needed to identify the unmet customer needs, see which of them we could address with our tech and do it better than the competition.
To identify and communicate these needs to the whole Cherry team, we decided to conduct quantitative (i.e. online surveys) and qualitative (i.e. in-depth interviews) research on the end-to-end experience people had with existent home security solutions and visualize them via an experience map.
My approach to experience mapping consists of three steps: Research, Map and Communicate. In this article, I’m going to walk you through each of them.
AUTHOR
Nick Komarov is a Shanghai-based designer with 10+ years of experience envisioning, conceptualizing, and designing innovative solutions for global clients in various industries.
CHERRY LABS
A startup working on the first human-centric AI home security system that protects people, not just homes.
Headquarters:
Cupertino, California
Founded: 2016
Team: 25 people
FOUNDERS: Max Goncharov, Nick Davidov
1. Research – Collect real customer data for the experience map
Experience maps aren’t based on guesses and assumptions; they are based on data acquired from real people via surveys, in-depth interviews, observations and desk research.
We had already surveyed about a hundred people and had discovered a lot of WHATs (e.g. the products on the market that were most popular and the features most used). What we were missing were the HOWs (how people buy and install home monitoring devices and how they use them over time) and the WHYs (why users decided to buy them in the first place, why they chose one product over the other and why they use certain features and ignore others). In-depth interviews and (surprisingly!) desk research can shed light on these questions and provide invaluable input for your experience map, so research is an absolute must. Here’s how I approach it.
Recruiting respondents
You need people to interview (duh!). Finding people who: a) meet your recruitment criteria and b) are willing to talk to you is essential but, alas, a time-consuming step. In my experience, it can easily take a couple of weeks or more, so plan for it. I can name three ways to recruit that I have tried:

It might be the simplest way out there. You tell the agency who you want to talk with, and they provide you a list of candidates to choose from. The downside? It’s expensive. In countries like the United States, it costs a lot, so unless you have a generous budget for research, you probably want to recruit by yourself.

You create an ad specifying demographics and other criteria, promise them some reward (e.g. a $50 Amazon gift card), run the ad for a week for a $100 and wait for people to reach out to you. It kind of works, but in my experience the conversion is very low, so I never rely solely on this approach.

Think of people you know who meet your recruitment criteria and ask your friends and teammates to do the same. Reach out to them, ask for an hour of their time. They rarely say no. Once you sign up first respondents, ask if they know anyone who’d be willing to talk to you. This is called “snowball recruitment” and also works well.
Conducting desk research while recruiting respondents
As you’re arranging the in-depth interviews, it’s usually a good idea to carry out some desk research. It helps you immerse yourself into the subject and gives you an impression of the stages of customer experience you’re investigating. The good news is that doing desk research is not difficult. I read product reviews on Amazon and watched unboxing videos on YouTube to learn how home monitoring solutions work, what customers like and dislike, and how they use them. I then laid out and interpreted these initial findings on Miro, making a solid foundation for the experience map to come.
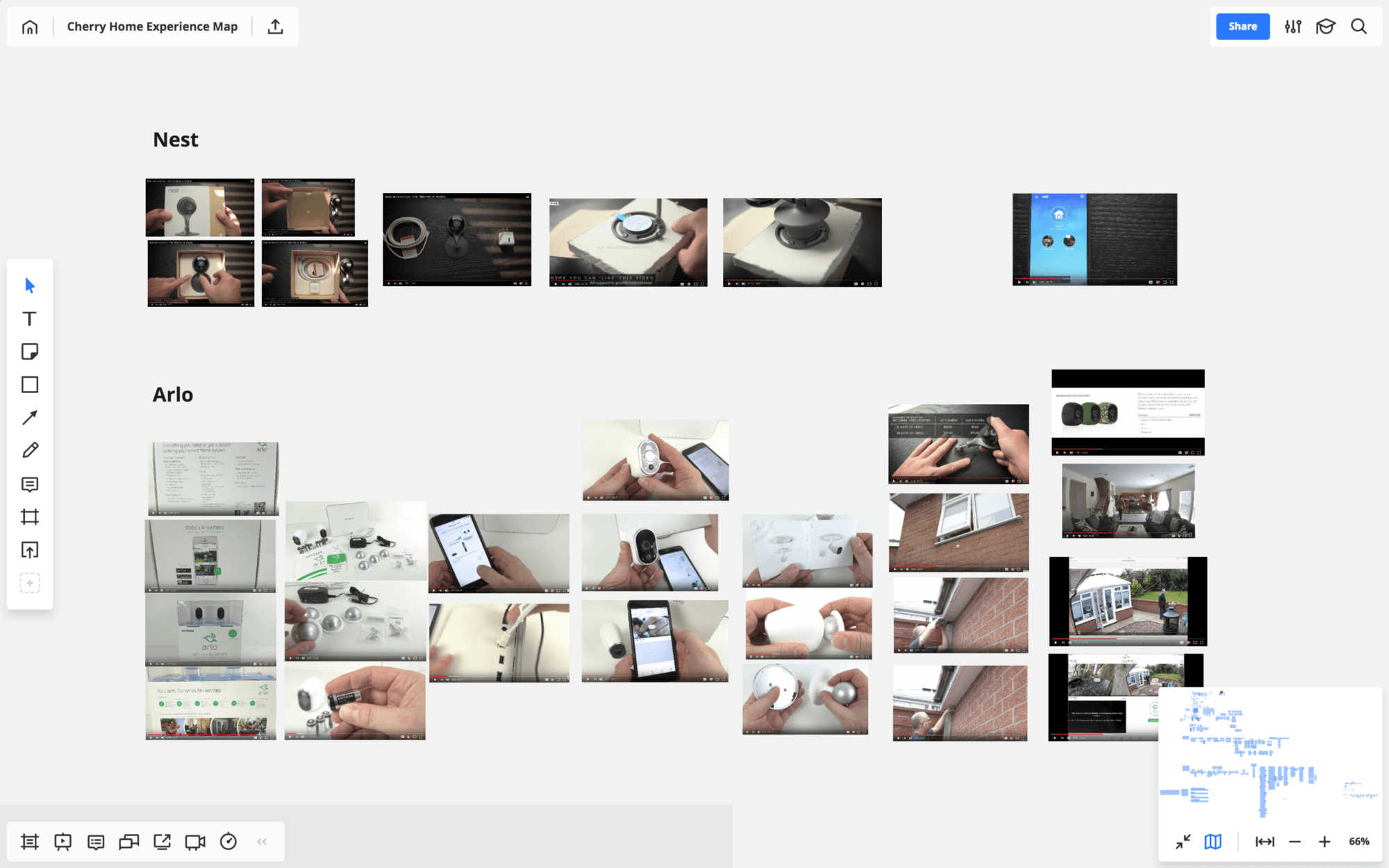
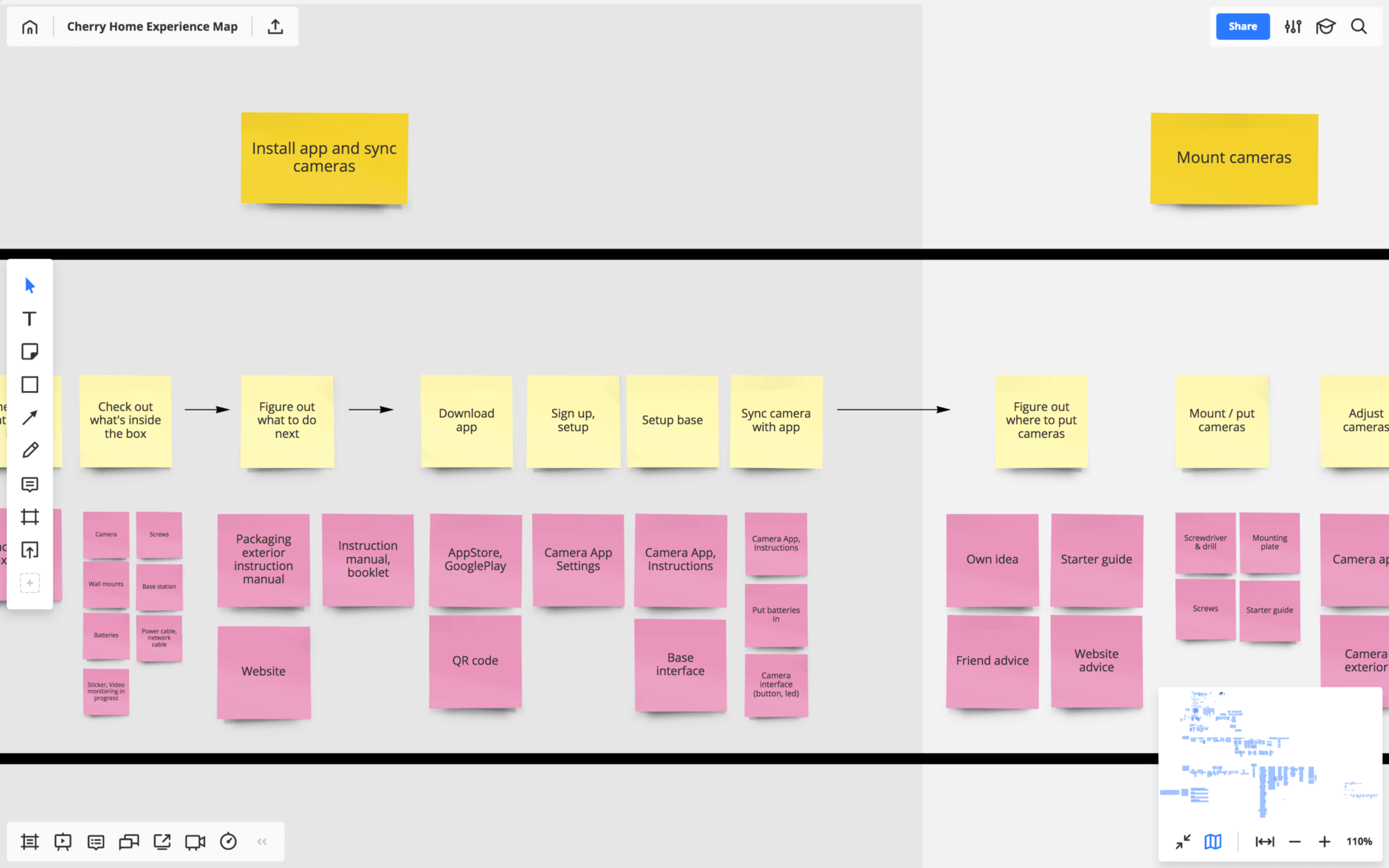
Preparing a discussion guide
It’s absolutely necessary to create a plan to use during the interviews. You don’t have to follow it word for word, but it’ll help you lead the interview in the right direction and make sure all the important questions are answered. After completing the desk research, I made a list of experience moments into which I wanted to get a firsthand customer perspective, as I thought there might have been some interesting opportunities for our product. With these in mind, I outlined the way the interviews could unfold.

Conducting interviews
No matter how you do your interviews, in person or via video call, make sure you take notes. Never rely on your memory – it will fail you. Taking notes and talking at the same time is tricky; that’s why it’s easier to conduct interviews with a partner. One of you leads the interview, and the other takes notes and makes sure nothing is missed. That said, I often conduct interviews all by myself. It takes practice but is doable. What I do is duplicate a master copy of the discussion guide and use it during the interview to type my notes in-line.

2. Map – Visualize research findings
Interpreting findings
It’s best to analyze and interpret the findings within a day or two after the interview while your memory is still fresh. Referring to your notes and using stickers, write down the responses and observations that you feel are going to be insightful and capable of sparking ideas within your team. One sticker means one response or observation. I like using direct quotes as they make the experience map more relatable and easier for your team members to imagine themselves in the customer’s shoes.
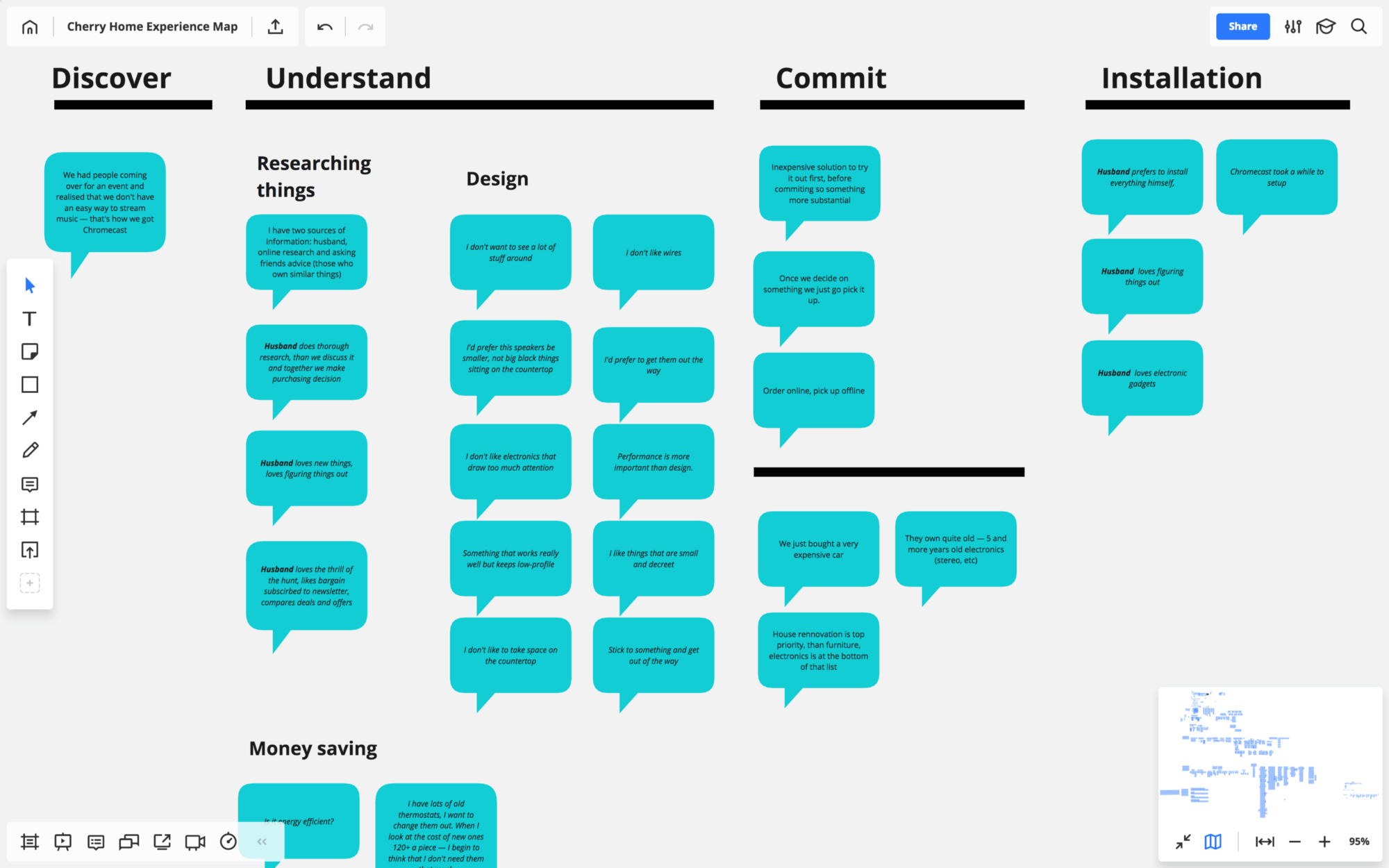
Outlining the experience map
Once you’ve got the notes from your interviews interpreted and written down on the stickers, you can start building your map. Depending on the project, you can either start working on the map right after the first interview if the customer journey in question is more or less known and clear, or wait until all of the interviews are finished if you’re investigating something that’s still a mystery to you.
In my experience, every map is always at least a little different from the previous one. Whenever I begin working on a new map, there are so many unknowns that I can never be sure how exactly it’s going to shape up. To deal with this ambiguity, I start with a universal structure – the bones of a map – and adjust and bend it as the project unfolds and more input flows in.
Here’s the structure I base all my maps on:
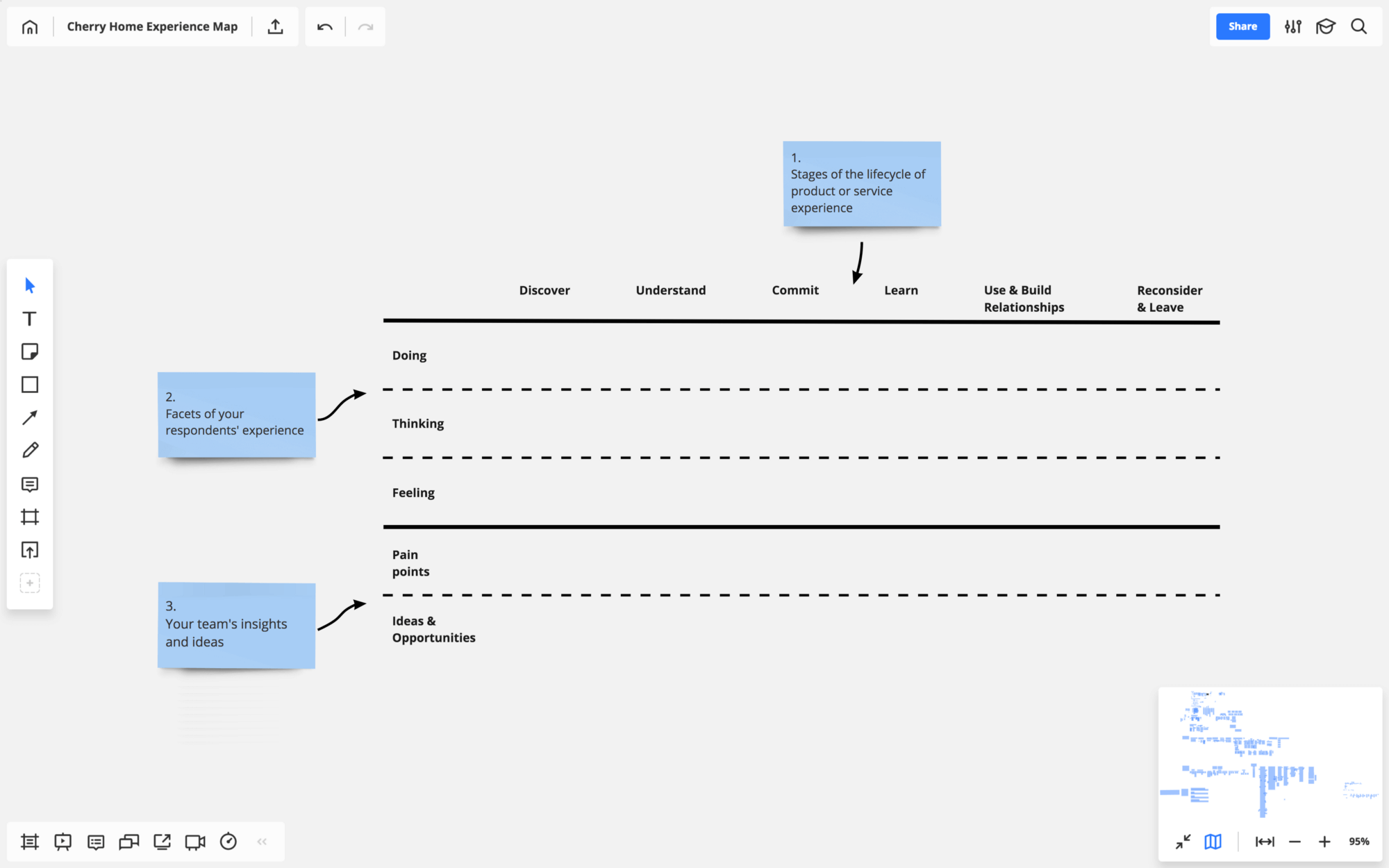
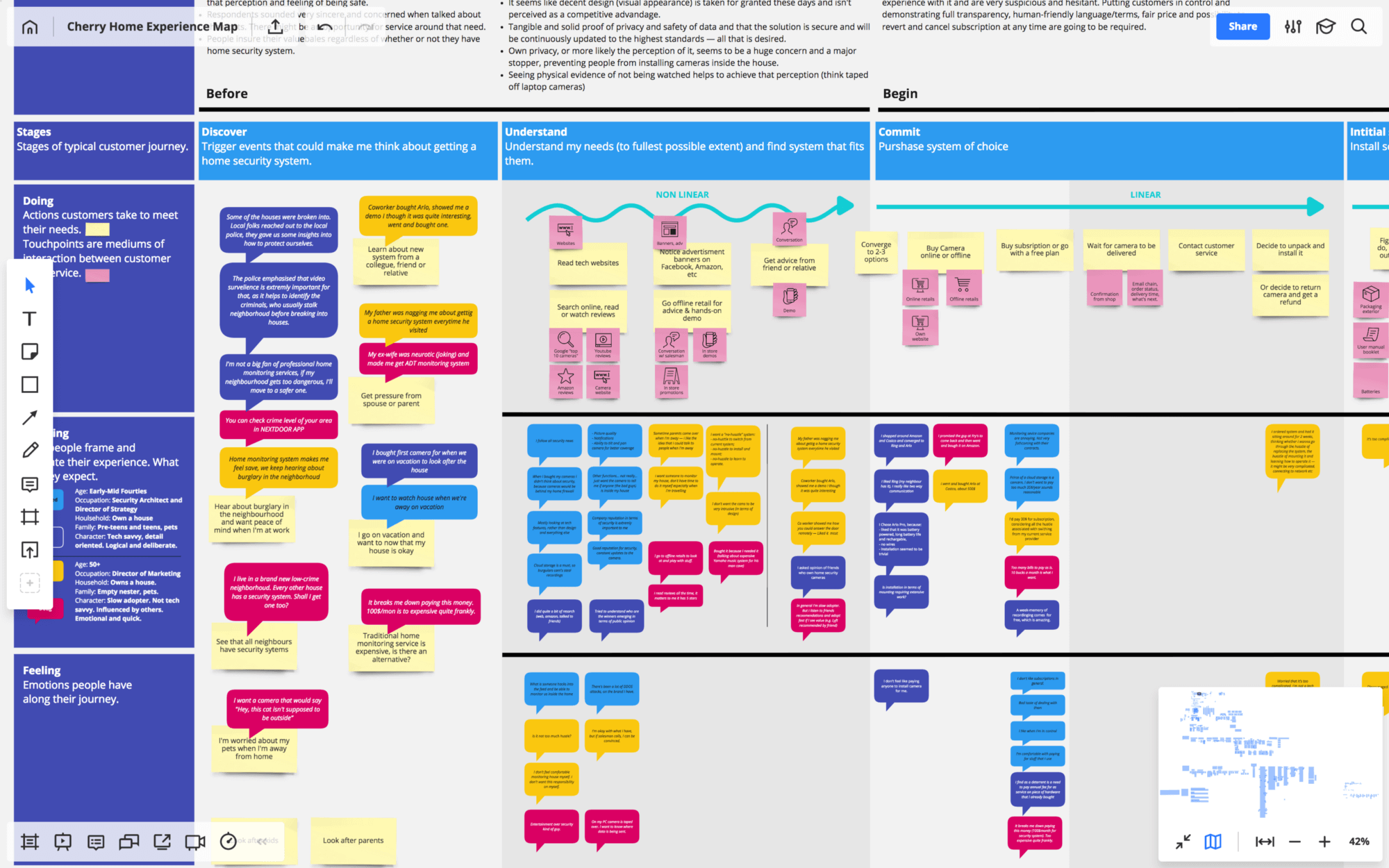
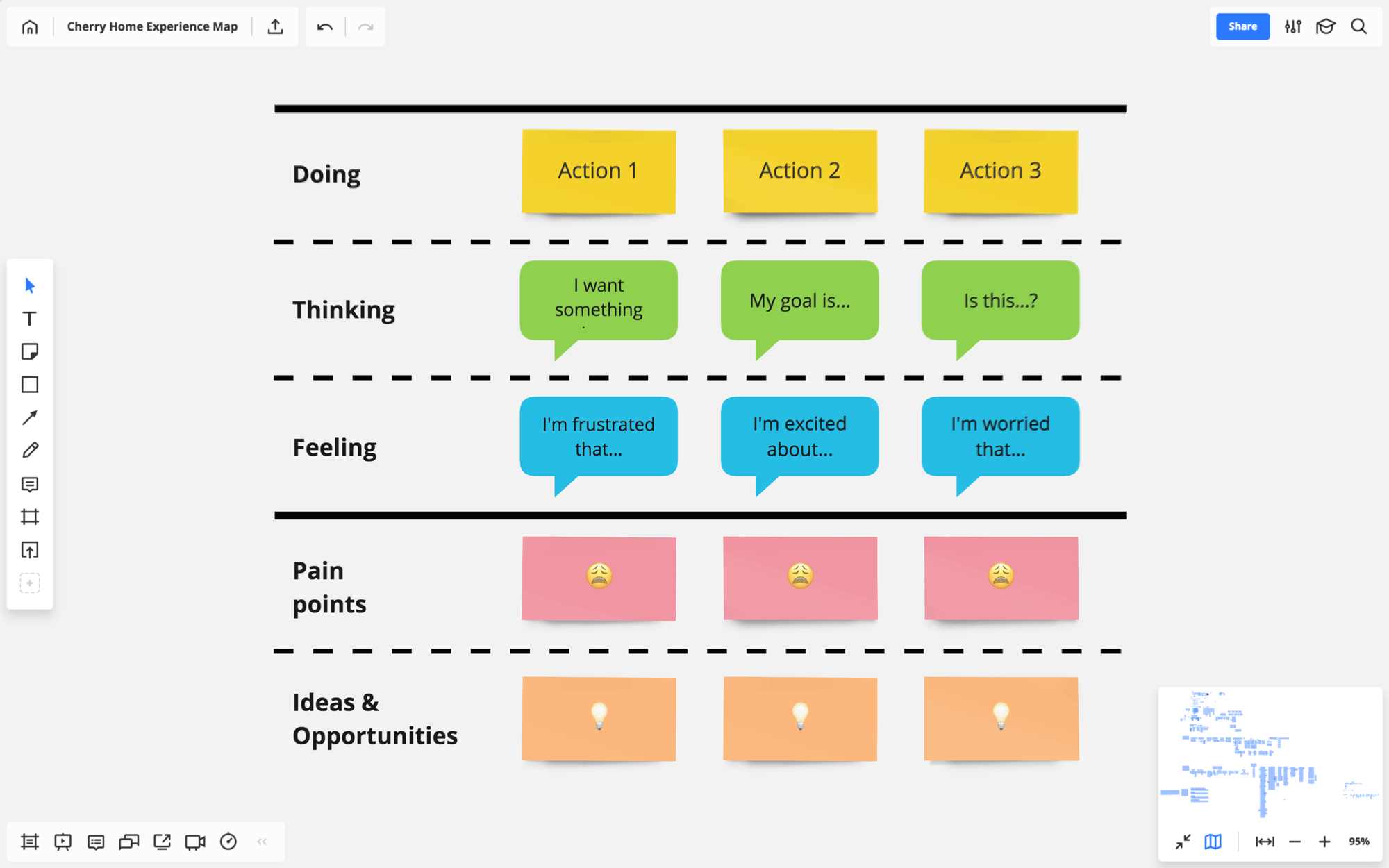
- Columns — the lifecycle of the product or service experience. These are the typical stages customers go through with most products and services.
- Primary swim lanes — the customer’s actions, thoughts and emotions. These are the facets of the experience you want to tell your team about.
- Secondary swim lanes — your and your team’s interpretations of everything from the primary swim lanes. Typically, these are the pain points and unmet needs, followed by ideas on how to address them and new design opportunities.
Building experience map

Based on the desk research and interviews, break down the lifecycle’s stages into more detailed steps, the actions customers perform and the touchpoints they use. Strike a balance between being overly specific and too vague. Keep asking yourself, “Is this relevant for our product? Are there any opportunities for us at this step? By looking at it, are my teammates going to learn anything they don’t already know?”

Paraphrase or map out the direct quotes from your interviews under the corresponding actions. This is the “empathic” component of your map, something that helps your team see what the subject in question really looks like through the eyes of the customer. This is what sparks ideas!
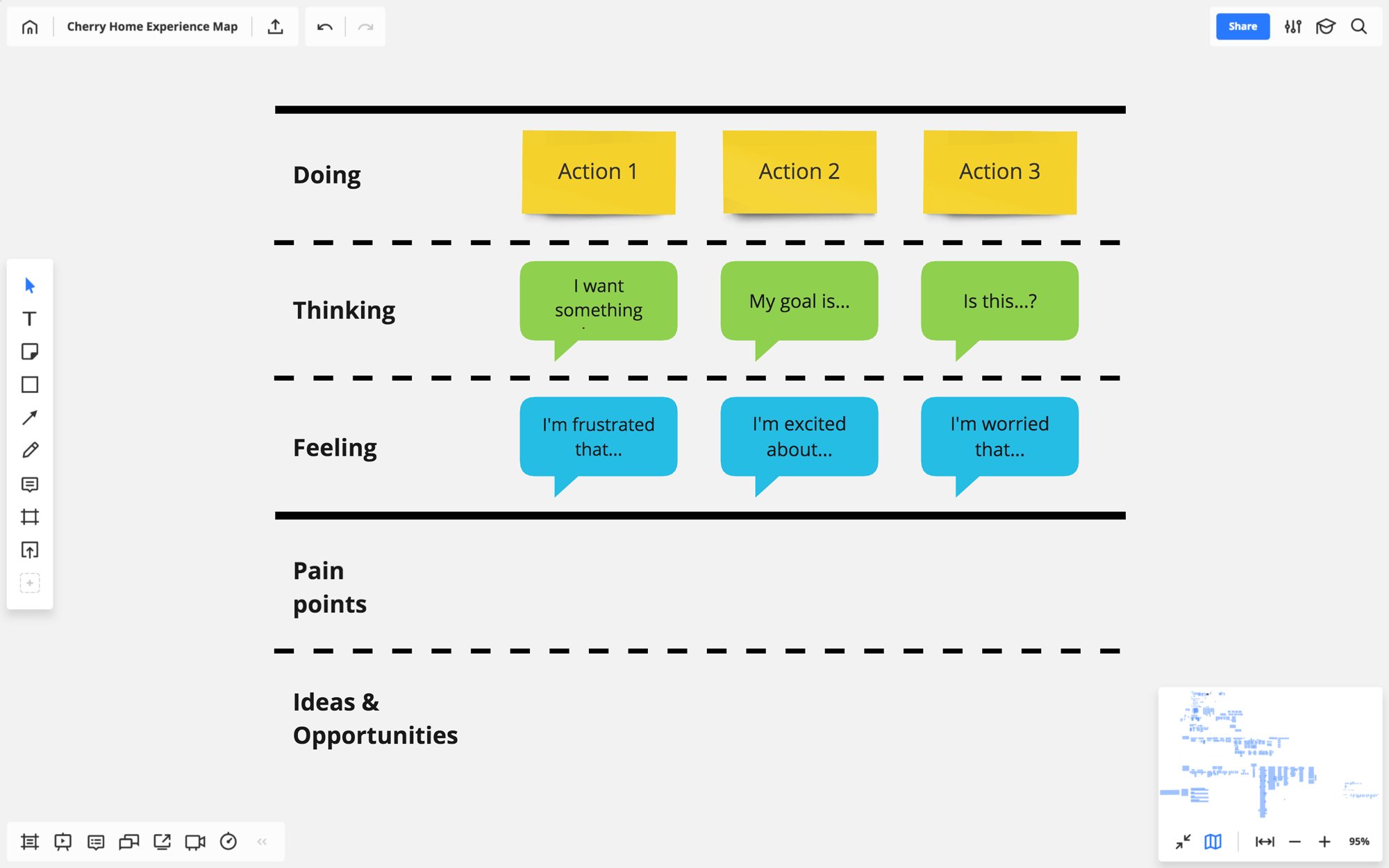
Do this for each column and voilà! You have a draft of your map. Now it’s time to bring in the rest of your team and kick off a discussion.
Looking for a tool for experience mapping?
Try Miro free, no strings attached
No credit card required
3. Communicate – Use experience stories to inspire ideas
It’s always good to remind yourself why you do mapping in the first place. Creating a cool-looking map, although it might be tempting, isn’t the goal. The goal is to ignite the idea generation process within your team by telling a compelling story about the actual experiences people have. Don’t waste time beautifying your map; start showing it to your team as early as possible to let the ideation begin!
Kicking off conversation around your map with the team
If people aren’t personally involved and invested into something, they tend to disregard and ignore it. So, if you don’t want your team to glance at your map once and forget it forever, you must make the team your co-authors. You must engage them into building the map with you. Here’s a few ways to do it:

Describe customers’ actions, thoughts and feelings at each step. This is when direct quotes from the interviews trigger empathy and make for a great story.

Start by vocalizing the ones that you have already spotted, and then ask your team one by one for their input based on what they’ve just heard. As they speak, write their comments down on stickers and plot them on the map. It’s extremely important that your teammates see their thoughts being noted and recorded.

In my experience, a good real-life story always sparks ideas, even when your team is very experienced in the subject and seems to know everything about everything. Brainstorm quickly how you might solve the identified problems and meet the unmet needs. At this point high-level ideas are enough. Don’t focus on their feasibility; just write them down, plot them on the map and revisit them later.
All of a sudden, your team is co-creating with you, which means there’s a good chance they will keep using the map in the future to inform their decisions. As long as you feel that the team is learning something new and generating ideas, continue developing and discussing the map.
We used our experience map to facilitate numerous discussions about what Cherry Home could be and the needs it could solve. As a result, we generated many high-level product ideas and created the first version of our product story. Today, half a year later, we keep referring to the findings and ideas captured in the map to inform decisions on the product features and the overall experience.
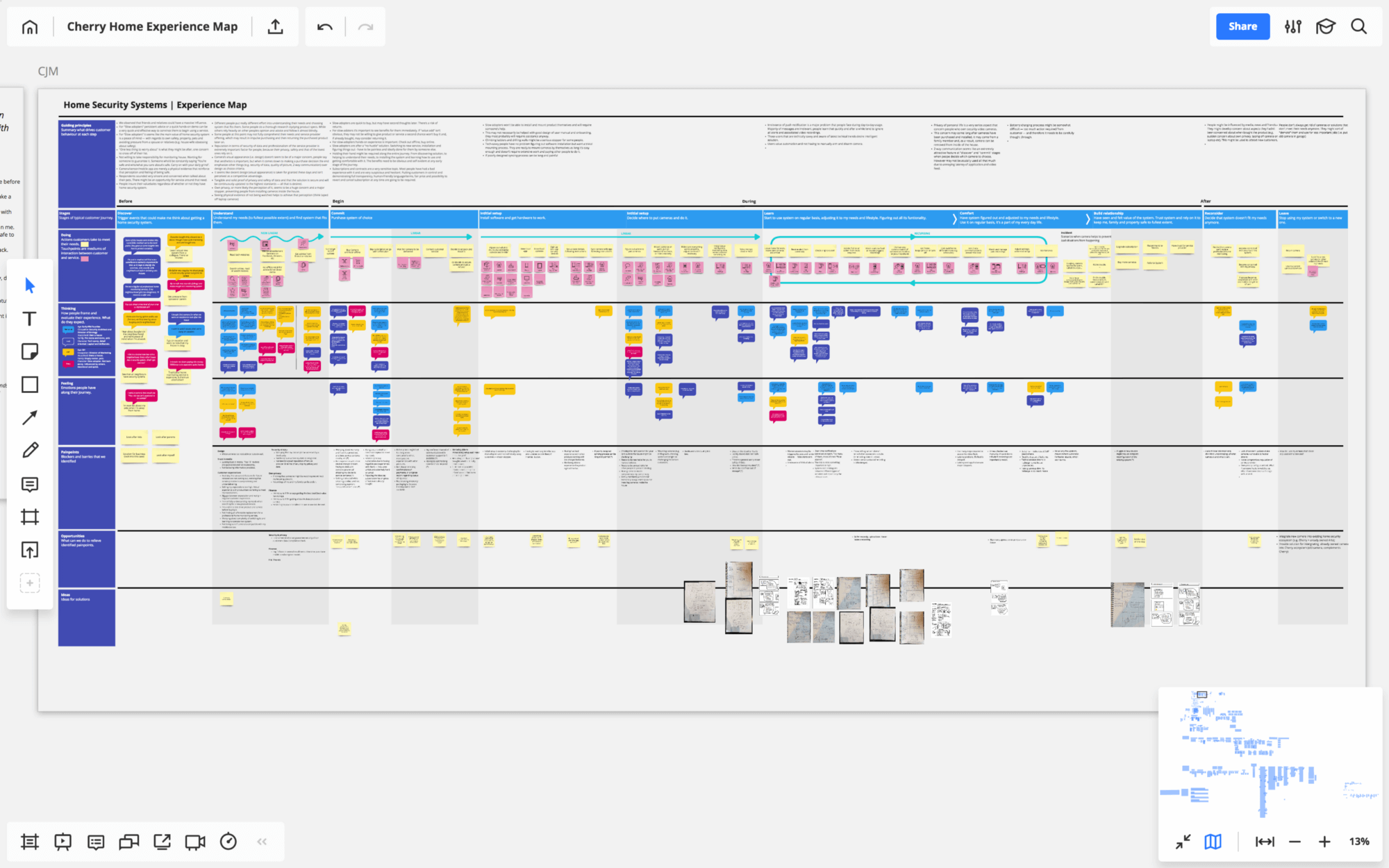
Takeaways






ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Nick Komarov
Nick Komarov is a Shanghai-based designer with 10+ years of experience envisioning, conceptualizing and designing innovative solutions for global clients in various industries. Adept at design thinking, organizational change, product and service design. To learn more about Nick’s work, you can follow him on Medium.